The challenges faced by IT personnel in today’s business world are more daunting than ever. Digital transformation requires us to embrace new emerging technologies to meet innovative business goals while also maintaining the stable operation of existing critical systems.
Last November at the International Supercomputing Conference, we witnessed an excellent solution to address these challenges. It is called the “Genoa,” which is the codename for the 4th generation AMD EPYC™ processors, specifically the AMD EPYC™ 9004 series.
This processor family offers a wide range of options, with some focusing on computational performance, some emphasizing low latency, and others providing more cores to help businesses meet expanding workload demands. It fully considers future enhancement capabilities and enables digital innovation.
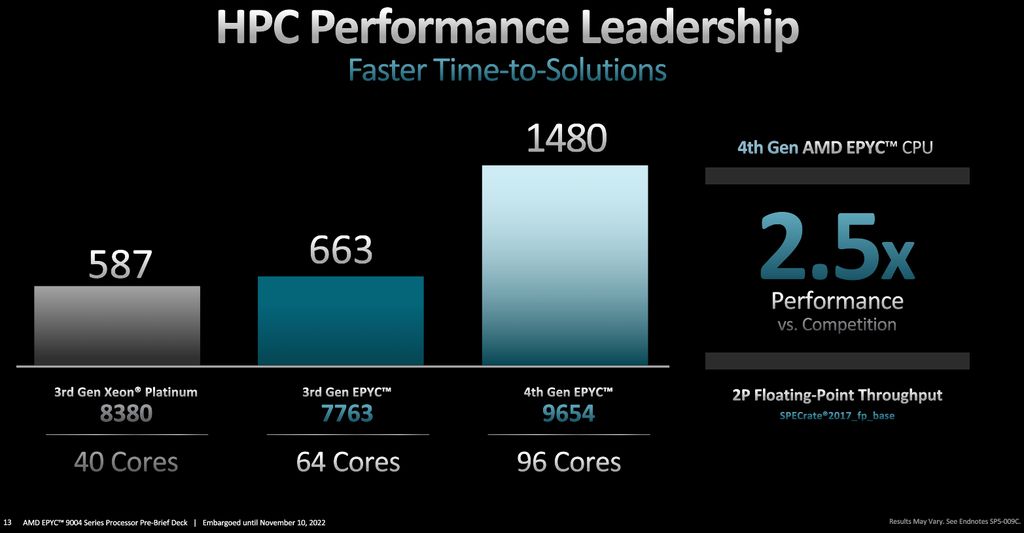
To meet different workload requirements, companies need to consider which processor architectures to use. For high-performance computing (HPC) and cloud applications, processors with high core counts are suitable for highly parallelized workloads.
For common enterprise applications, a balance needs to be struck between processor and I/O capabilities. Applications such as artificial intelligence (AI), data analysis, structured or unstructured data applications require powerful and fast cores as well as accelerated mathematical computations. On the other hand, network infrastructure, information security, and edge application services require cost optimization for widespread and secure deployment.
Decoding the Numbers of EPYC Models
The AMD EPYC™ 9004 series processors can fulfill these diverse requirements. The series uses a different naming logic, where the names consist of four digits plus a suffix letter. The second digit represents the number of cores, the third digit represents performance, and the suffix letter indicates specific processor features.
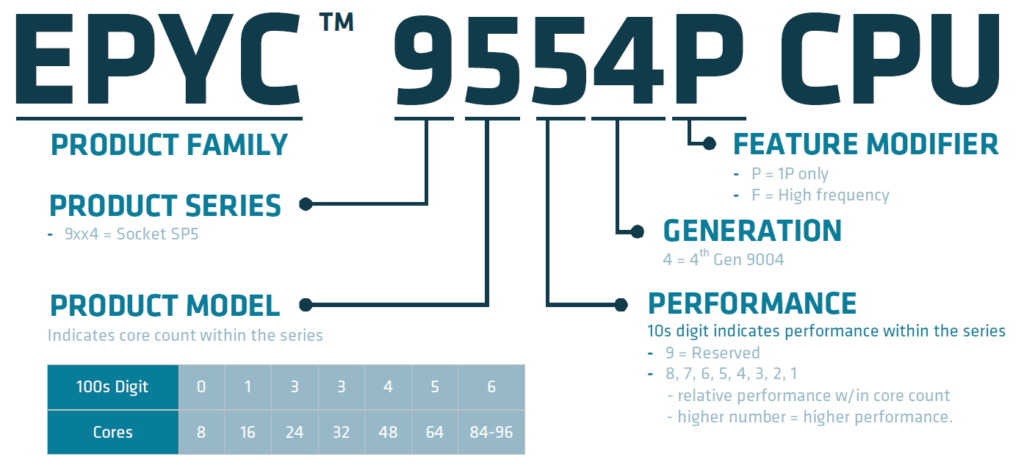
For example, processors like 9474F, 9374F, 9274F, or 9174F with the “F” suffix highlight high performance, with boost frequencies exceeding 4GHz. Additionally, processors like 9654, 9634, 9554, 9534, or 9454 emphasize high core counts, with 9654 having the highest number of 96 cores.
For processors like 9354, 9334, 9254, 9224, and 9124, which have two digits smaller than 94 and without the “F” suffix, they are designed for balanced computing performance and energy efficiency. These processors, such as the 32-core 9334, the 24-core 9254 and 9224, and the 16-core 9124, have a low thermal design power (cTDP) ranging from 200 to 240 watts.
Lastly, the products with a suffix “P” have the same core count, frequency, and cache memory as the ones without the “P” suffix, but they can only be used in single-socket servers and are offered at a more favorable price, attracting customers to use more energy-efficient single-socket solutions.
Unprecedented Performance and Efficiency of Zen 4
One might wonder how the AMD EPYC™ 9004 series processors can address so many innovative aspects. The key lies in their “hybrid multi-chip architecture,” which means that the Zen 4 processor cores and I/O functions are separated into different chips, allowing each component to be developed using the most suitable process. This approach enables AMD to treat the processor core complex and I/O complex as independent entities, optimizing their design and manufacturing processes separately. This results in enhanced performance, power efficiency, and scalability.
The Zen 4 processor cores are built using the advanced 5nm process technology, which enables them to deliver higher clock speeds, increased instructions per cycle (IPC), and improved power efficiency compared to previous generations. The Zen 4 architecture also introduces new features and enhancements, such as an expanded L3 cache, improved branch prediction, and upgraded security features, providing a significant boost in performance for a wide range of workloads.
On the other hand, the I/O complex is built using the mature 7nm process technology. This separation allows AMD to focus on optimizing the I/O capabilities, including memory controllers, PCIe lanes, and high-speed connectivity options. The AMD Infinity Fabric interconnect technology ensures efficient communication between the processor cores and the I/O complex, minimizing latency and maximizing data transfer rates.
Benefits of EPYC 9004 4th-Gen CPUs for Businesses

With its massive 96-core-count in a single processor, the new AMD Genoa processors will allow organizations to reduce their physical footprint by deploying fewer servers while leveraging more powerful servers. This brings greater flexibility to data center ecosystems and helps them to reach sustainability and future-proofing goals.
Organizations will be able to benefit from their “all-in” feature set, with options to choose a model with the core count and frequency that best suits their needs. Moreover, the 4th Gen AMD EPYC processors now support DDR5 memory and PCIe Gen 5, both of which are vital for AI and ML applications. Of course, enterprise SSD vendors are chomping at the bit to get their drives out to the mainstream, unlocking twice as much bandwidth potential as Gen 4.
Unleash next-level server performance with AMD EPYC™ Genoa
AMD built their new EPYC processors with a huge focus on enhanced security, particularly with expanding AMD Infinity Guard, the company’s set of features that offers both physical and virtual layers of protection to their CPUs.
Additionally, features like Secure Boot, Secure Memory Encryption (SME), and Secure Encrypted Virtualization (SEV) help safeguard virtualized environments and prevent unauthorized access, which helps customers keep their data secure whether it’s stored locally, in the cloud, or residing in storage.
The flexibility and scalability of the AMD EPYC™ 9004 series processors make them suitable for a wide range of applications and deployment scenarios. From high-performance computing (HPC) clusters and data centers to cloud computing infrastructure and edge computing deployments, these processors provide the necessary power, performance, and security features to meet the evolving needs of modern businesses.


