DNS name servers are used for name resolution from a server in all operating systems. In most Linux Operating systems, these DNS servers are specified in the file /etc/resolv.conf. This file contains one nameserver line which defines the DNS server.
This file can be viewed and the DNS nameservers edited by using the steps given below:
Open the file using any editor.
# vi /etc/resolv.conf

Add lines for the name servers that need to be used.
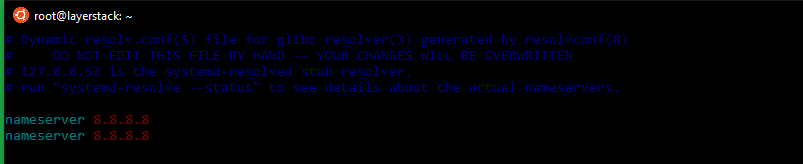
Here the common Google nameservers 8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4 have been used.
In modern Linux, this file is indirectly managed by the systemd-resolved service, and in some cases by the network service (by using initscripts or NetworkManager). Hence, manually changed values do not last or will get revoked after a reboot. To resolve this, the resolvconf utility can be installed and used to make the changes permanent. The below steps can be used for this.
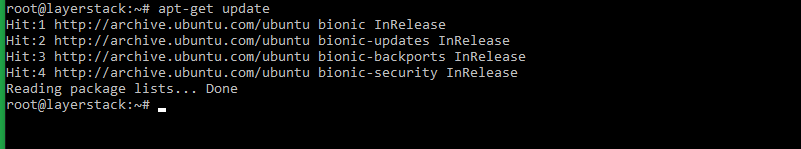
Run update before proceeding with the installation.
# apt-get update
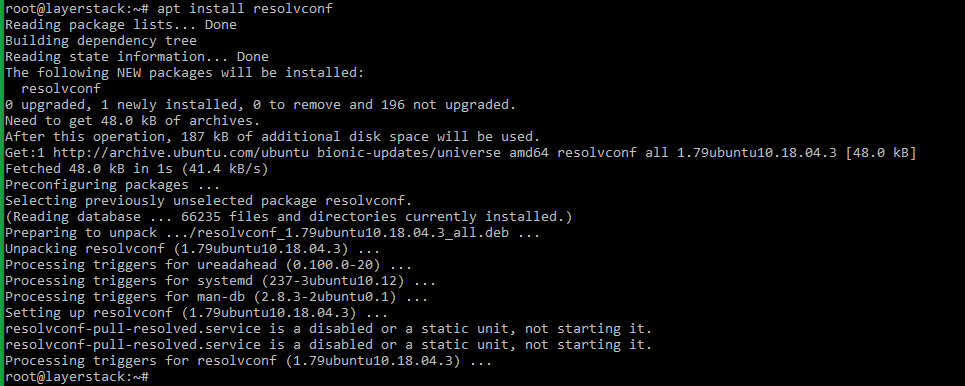
Install resolvconf by executing the below command.
# apt install resolvconf
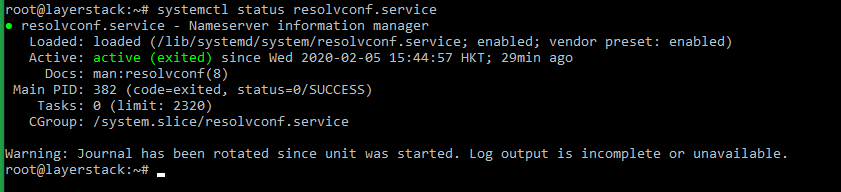
Verify the service status.
# systemctl status resolvconf.service
If the service is not started, it can be started using the below commands:
# systemctl start resolvconf.service
# systemctl enable resolvconf.service
# systemctl status resolvconf.service
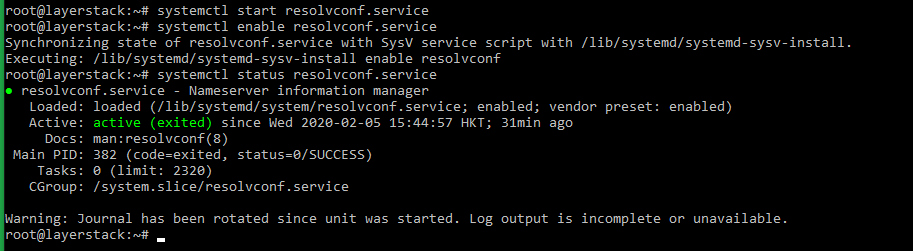
Set up permanent DNS nameservers.
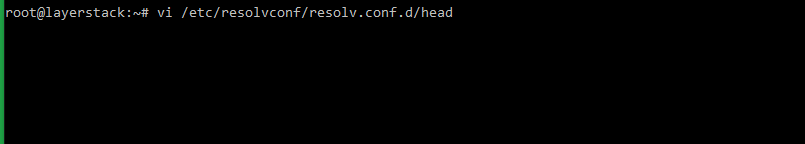
# vi /etc/resolvconf/resolv.conf.d/head
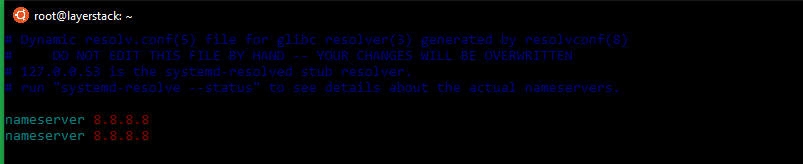
Here the common Google nameservers 8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4 have been used.
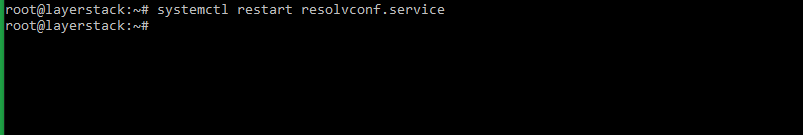
Restart the service.
# systemctl restart resolvconf.service
Related Tutorials