SSH (Secure shell) is a cryptographic network protocol used to connect to a remote server securely and it transfers the data in encrypted form between the host and the client.
The default TCP port for SSH is 22, and changing this default port to the other, can prevent automated bots and malicious users from being brutally forced into the server.
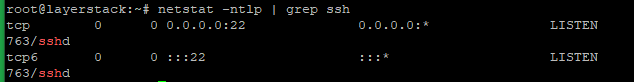
Before changing the default SSH port number, can check the current port with the below command.
# netstat -ntlp | grep ssh
This guide will describe the steps to change the SSH port and add the new custom SSH port in the firewall in the Linux server.
To change the SSH port
Open the main SSH daemon configuration file /etc/ssh/sshd_config.
# vi /etc/ssh/sshd_config
Now search line begins with Port 22 and adds a hashtag (#) in front of that line. Then add a new Port line below with the custom port as shown in the image.
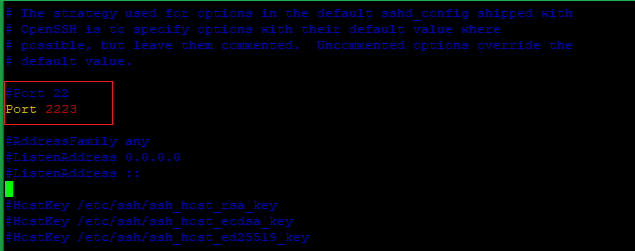
Note: Replace the sample port number 2223 with the custom port number that needs to be set.
Save and exit.
To add the new custom SSH port in the server firewall
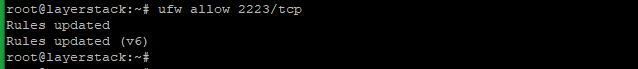
To set up a firewall with UFW ( Ubuntu/Debian ).
# ufw allow 2223/tcp
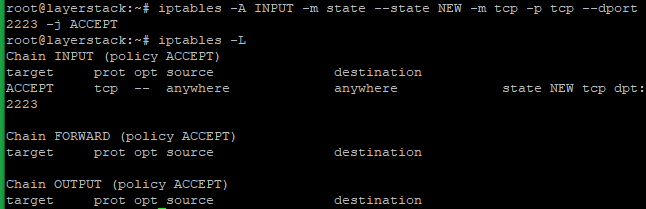
To add in IPTables and verify ( All Linux OS ).
# iptables -A INPUT -m state --state NEW -m tcp -p tcp --dport 2223 -j ACCEPT
# iptables -L
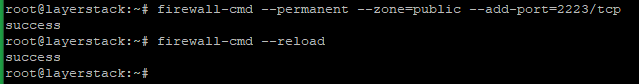
To add in FirewallD ( CentOS 7/8 ).
# firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-port=2223/tcp
# firewall-cmd --reload
Note: Replace the sample port number 2223 with the custom port number that needs to be set.
Restart the SSH daemon for the changes to take effect
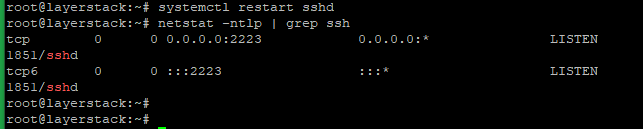
Run the below commands to restart the SSH daemon and verify that the port changed.
# systemctl restart sshd
# netstat -ntlp | grep ssh
Related Tutorials