How to enable TLS 1.3 in Nginx service of CentOS Cloud Servers (with Cipher Suites included)
Transportation Layer Security (TLS) is a cryptographic protocol and it provides the security for the delivery of data over the internet. TLS 1.3 is faster than TLS 1.2 because the handshake for TLS 1.3 is reduced to just one round-trip.
This can easily be enabled in a Linux-based server. This guide outlines the basic steps involved in a Linux CentOS server (provided Nginx service is already installed in the server).
Requirements:
- Server running on CentOS 8.
- A valid domain name and properly configured A/AAAA/CNAME DNS records.
- A valid TLS certificate. Here using from Let’s encrypt.
- Nginx version 1.13.0 or greater.
- OpenSSL version 1.1.1 or greater.
Before the beginning,
Check the CentOS version by using the below command.
# cat /etc/centos-release
By using the below command ensure that the server is up to date.
# dnf update
Install the needed packages by using the below command.
# dnf install -y socat git wget unzip
Step A. Install the acme.sh client and obtain a TLS certificate from Let's Encrypt.
acme.sh is used to install, renew and remove SSL certificates and it is written purely in Shell (Unix shell) language, compatible with bash, dash, and sh shells.
Install acme.sh with the below commands.
# git clone https://github.com/acmesh-official/acme.sh # cd acme.sh # ./acme.sh --install –accountemail [email protected] # cd ~ # source ~/.bashrc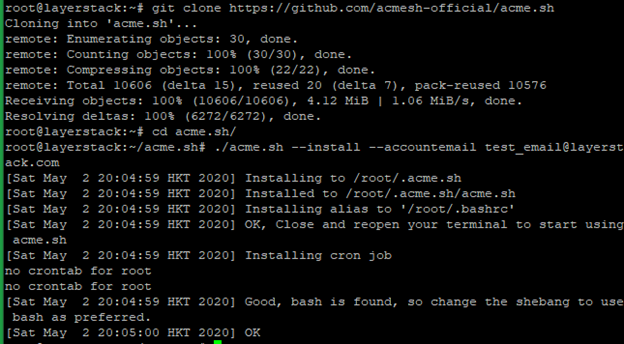

NOTE: Replace the mail account with your mail account name.
Check the version of acme.sh.
# acme.sh --version
Obtain RSA and ECDSA certificates for the domain.
# RSA # acme.sh --issue --standalone -d example.com --keylength 2048 # ECC/ECDSA # acme.sh --issue --standalone -d example.com --keylength ec-256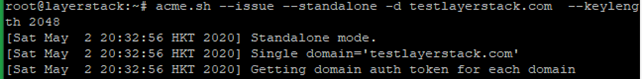
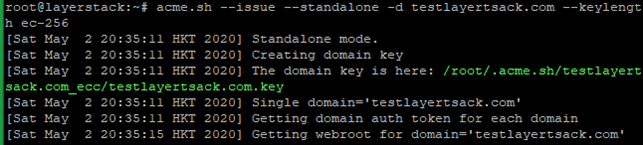
Create directories to store your certs and keys in then, install and copy certificates to /etc/letsencrypt.
# mkdir -p /etc/letsencrypt/testlayerstack.com # mkdir -p /etc/letsencrypt/testlayerstack.com_ecc
# acme.sh --install-cert -d testlayerstack.com --cert-file /etc/letsencrypt/testlayerstack.com/cert.pem --key-file /etc/letsencrypt/testlayerstack.com/private.key --fullchain-file /etc/letsencrypt/testlayerstack.com/fullchain.pem # acme.sh --install-cert -d testlayerstack.com --ecc --cert-file /etc/letsencrypt/testlayerstack.com_ecc/cert.pem --key-file /etc/letsencrypt/testlayerstack.com_ecc/private.key --fullchain-file /etc/letsencrypt/testlayerstack.com_ecc/fullchain.pem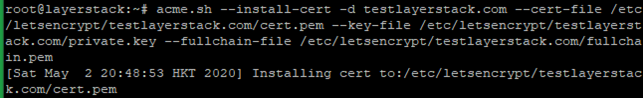
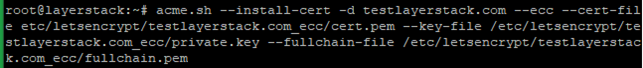
After running the above commands, your certificates and keys will be in the below-mentioned locations:
RSA: /etc/letsencrypt/testlayerstack.com ECC/ECDSA: /etc/letsencrypt/testlayerstack.com_ecc
Step B. Configure Nginx for TLS 1.3
Run the below command to install the Nginx.
# dnf install nginx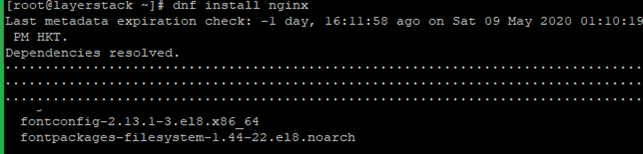
Check the Nginx version then, start and enable using the below commands.
# nginx -v # systemctl start nginx.service # systemctl enable nginx.service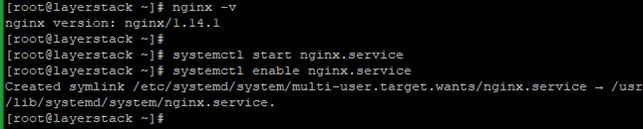
Run the below command and add the following basic configurations in that file.
# vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/testlayerstack.com.conf server { listen 443 ssl http2; listen [::]:443 ssl http2; server_name testlayerstack.com;# RSA ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/testlayerstack.com/fullchain.cer; ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/testlayerstack.com/testlayerstack.com.key; # ECDSA ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/testlayerstack.com_ecc/fullchain.cer; ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/testlayerstack.com_ecc/testlayerstack.com.key; ssl_protocols TLSv1.3 TLSv1.2; ssl_ciphers 'ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE- ECDSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-RSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256'; ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;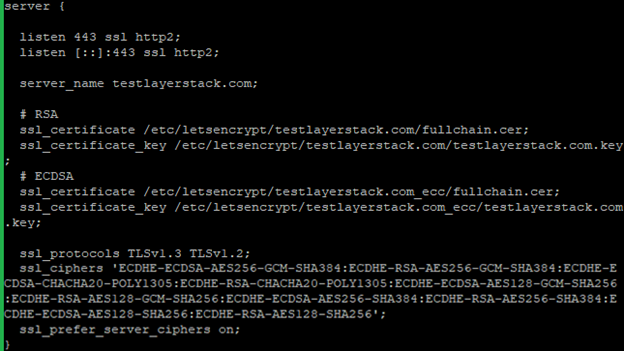
Save the file and exit.
NOTE: Replace testlayerstack.com in commands with your valid domain name.
Reload Nginx to activate in the new configuration.
Now you can verify TLS 1.3 by using any browser dev tools or SSL Labs service such as given below.
https://www.ssllabs.com/ssltest/
