Keeping servers up-to-date ensures that security patches and bug fixes get applied to all the packages on them. Using dnf-automatic will automate this process by synchronizing package metadata as needed, and then checking for updates available and downloads and installing them, and will never have to worry about forgetting to update your server again.
The advantage is the server will be more secure and frequent updates, bug fixes and security patches are installed on time to prevent vulnerabilities. DNF has become a powerful package manager for Linux systems and the key benefit of dnf is the option to retrieve security information very easily.
This guide outlines the basic steps on how to install and configure dnf-automatic in AlmaLinux, RockyLinux, CentOS & Fedora.
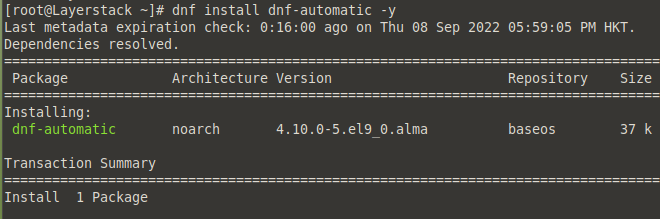
Install the dnf-automatic package.
# dnf install dnf-automatic -y
Configure automatic.conf file.
Open the configuration file and change the following:
# vim /etc/dnf/automatic.conf
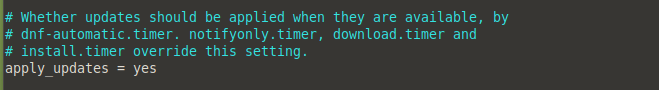
By default, dnf-automatic downloads updates without applying them automatically:

Apply updates to your server after it has downloaded them, find the apply_updates parameter, and change it to yes:
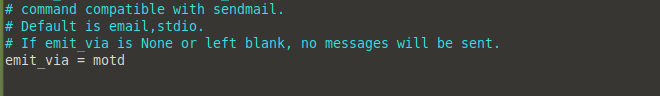
Set the emit_via parameter to motd. This tells you about any updates that have been installed, every time you log in to your server:
Save and exit the file when you've finished editing it.
Before continuing, run the dnf-automatic command manually to make sure that there are no errors in your configuration file.
# dnf-automatic

Enable the timer with the systemctl command.
# systemctl enable --now dnf-automatic.timer
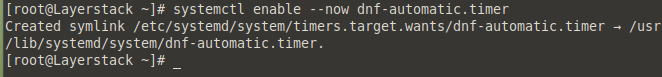
Configure the timer, and change the timer to a more convenient schedule.
# vim /etc/systemd/system/timers.target.wants/dnf-automatic.timer

Change the time specified after the OnCalendar parameter.
For example, change the 6:00 for the preferred time:

After making changes to the timer file, reload the systemd daemon to apply the changes.
# systemctl daemon-reload

Check the new timer configuration.
# systemctl daemon-reload

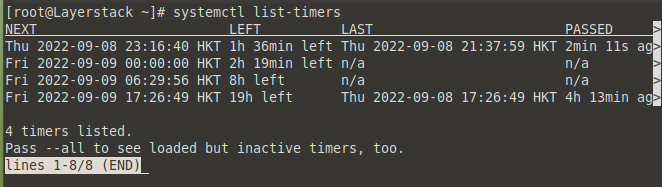
To check if the new timer configuration worked, list all the timers on the system.
# systemctl list-timers