The unsupported operating systems versions will no longer receive security updates. If keeping the outdated version, some unauthorized people may target those outdated operating systems because of their vulnerability, allowing them to breach the server and gain personal information. The best possible way to prevent them is to update your operating system to the latest version regularly.
The below steps can be followed to update the version for CentOS, Ubuntu & Debian.
Check the current CentOS version in the server using the following command.
# cat /etc/redhat-release
Once checked, then need to install EPEL Repository in the server.
# yum install epel-release -y
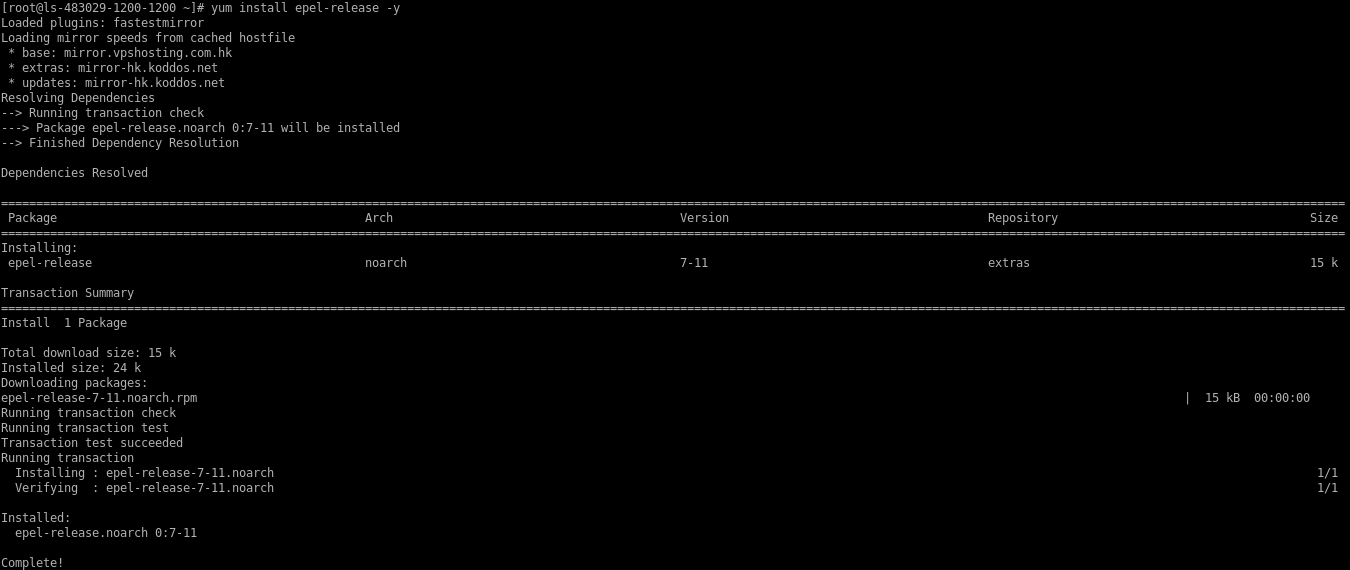
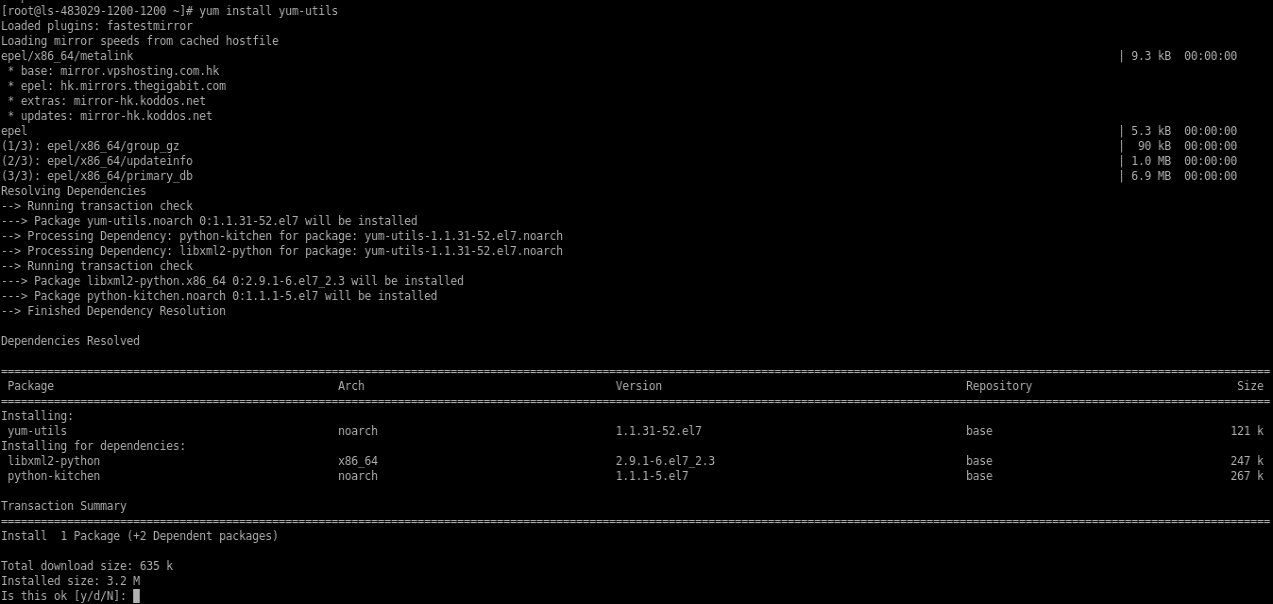
Install yum-utils in the server.
# yum install yum-utils
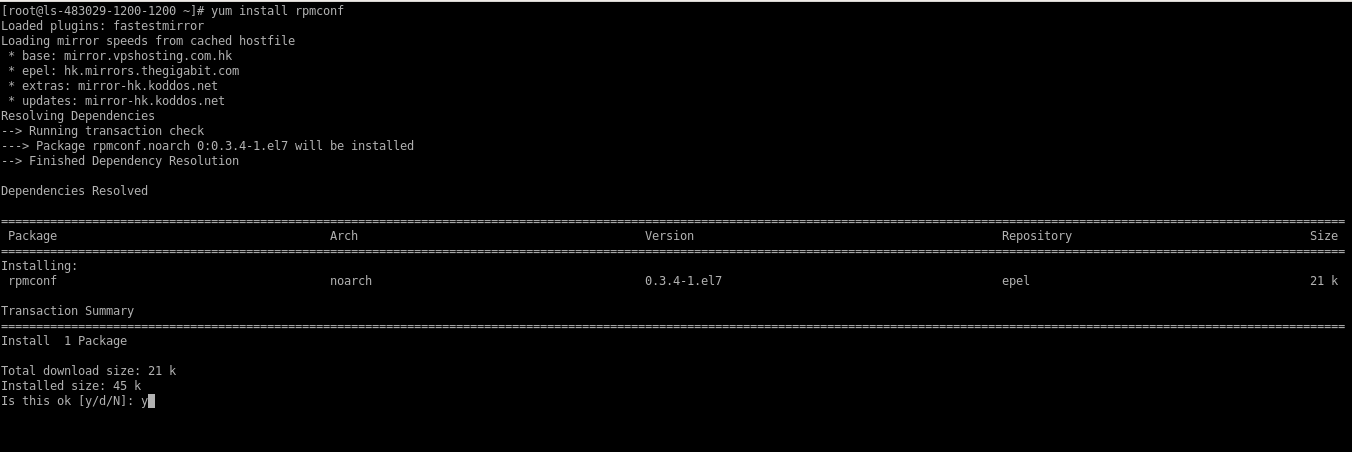
Then need to resolve RPM packages in the server.
# yum install rpmconf
AND
# rpmconf -a

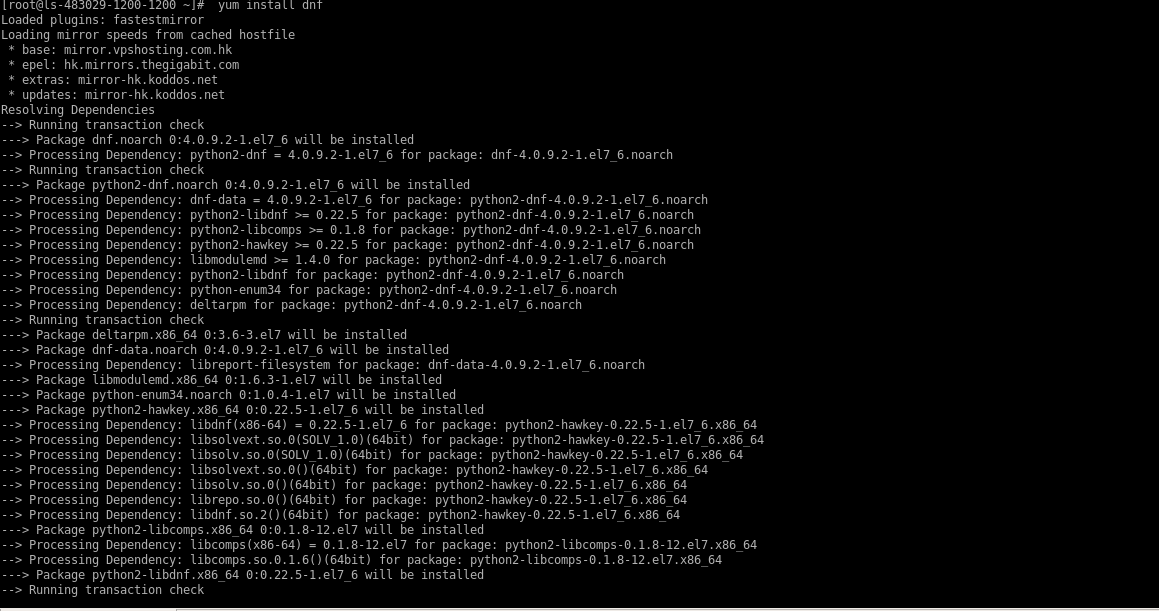
Install dnf in the server, dnf is the default package manager for CentOS 8.
# yum install dnf
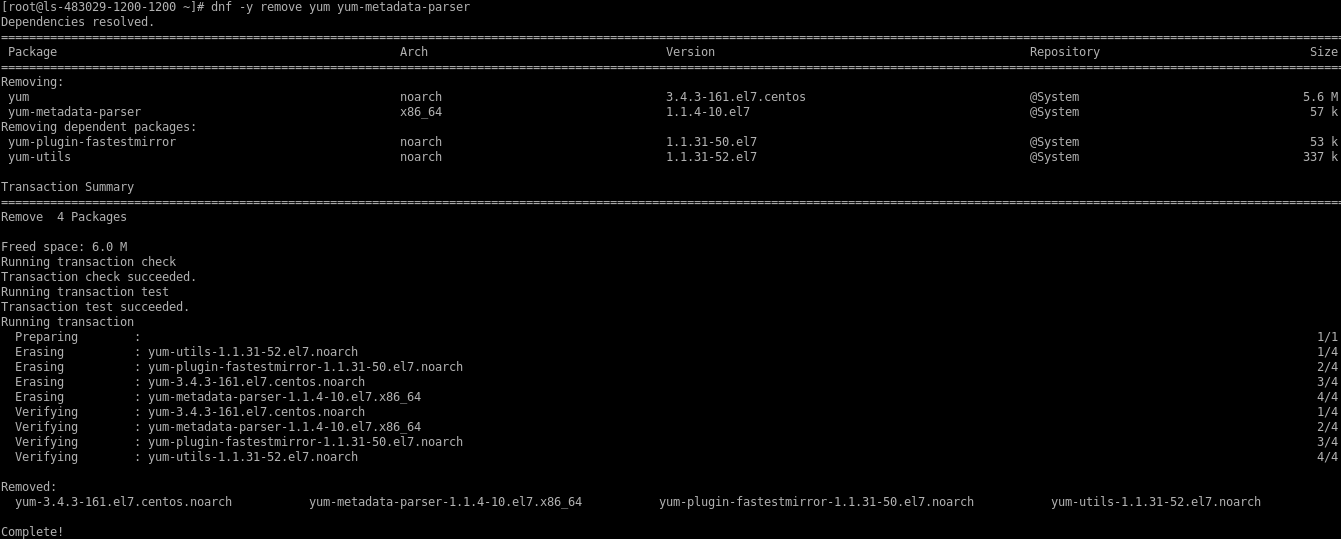
Remove the yum package manager from the server.
# dnf -y remove yum yum-metadata-parser
AND
# rm -Rf /etc/yum

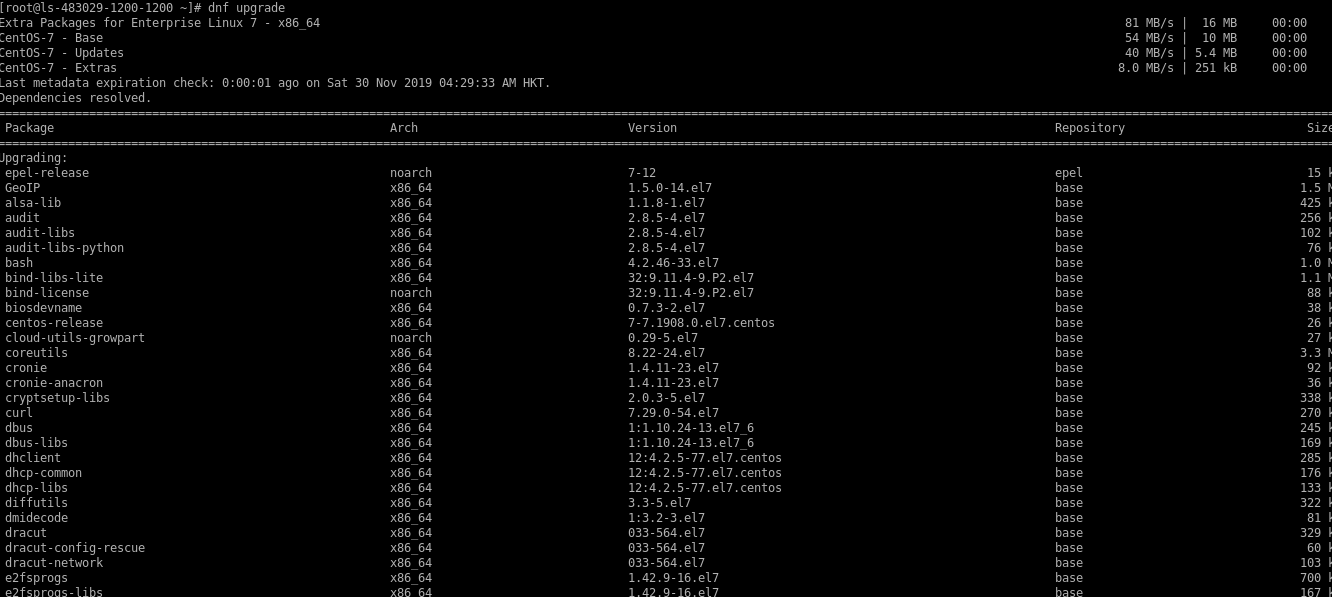
Upgrading CentOS 7 to CentOS 8.
# dnf upgrade
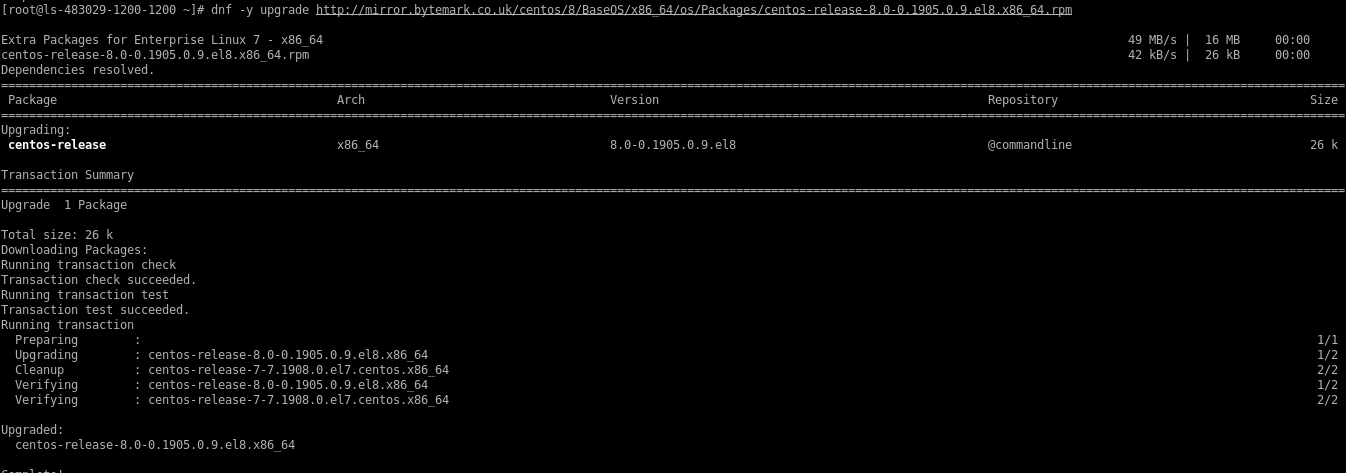
Install CentOS 8 release packages on the server.
# dnf -y upgrade http://mirror.bytemark.co.uk/centos/8/BaseOS/x86_64/os/Packages/centos-release-8.0-0.1905.0.9.el8.x86_64.rpm
Remove all the temporary files.
# dnf clean all

Need to remove the old kernel core of CentOS 7.
# rpm -e `rpm -q kernel`

Remove conflicting packages.
# rpm -e --nodeps sysvinit-tools
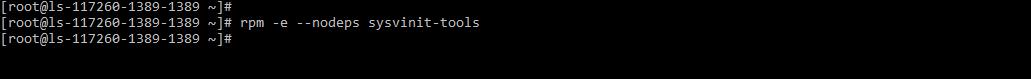
Launch the CentOS 8system upgrade as shown.
# dnf -y --releasever=8 --allowerasing --setopt=deltarpm=false distro-sync
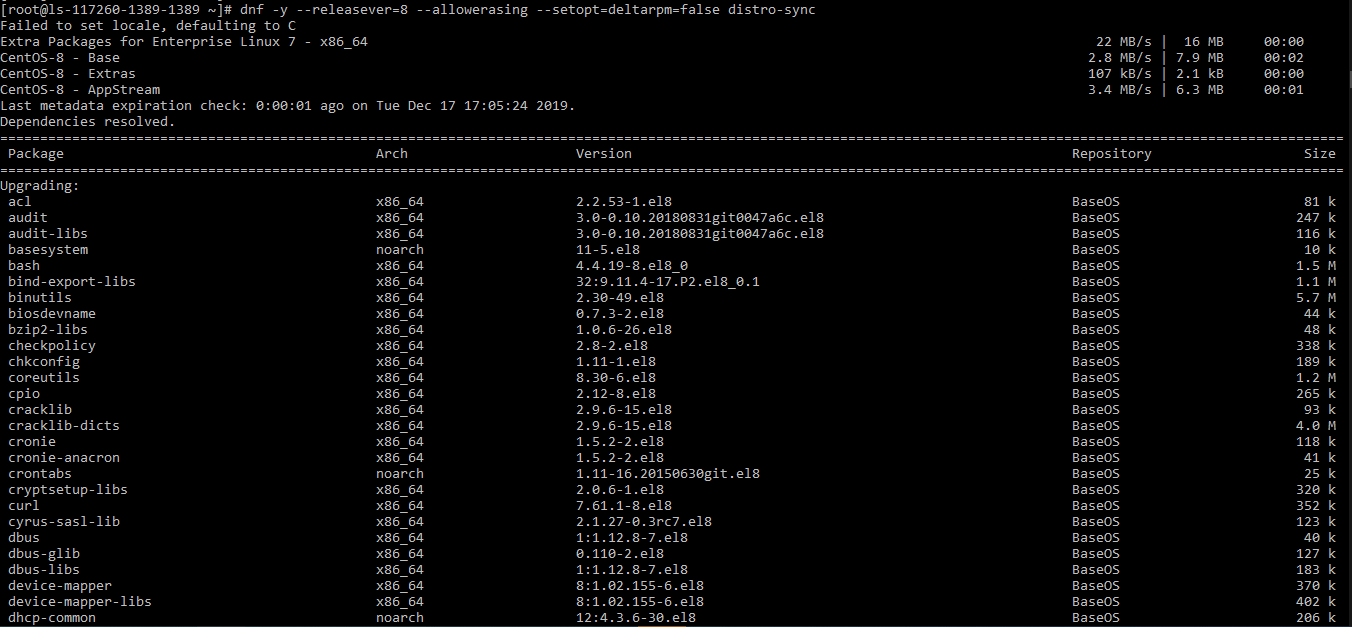
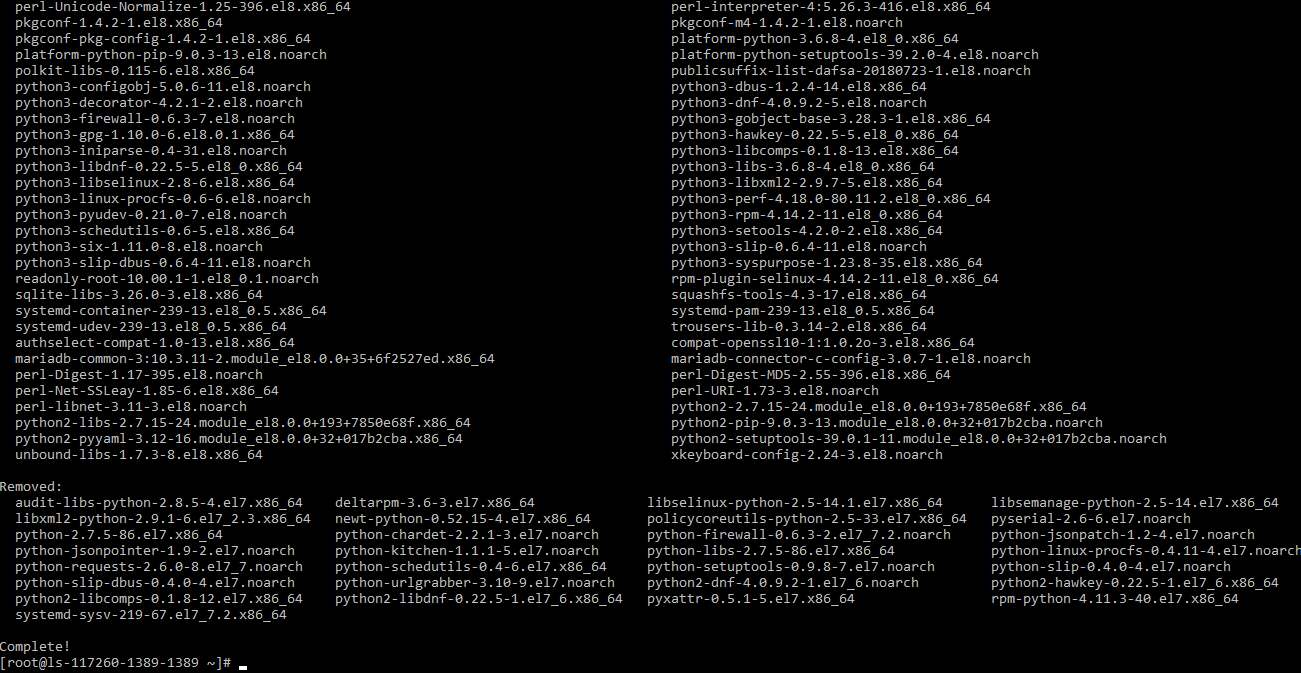
Install new Kernel Core for CentOS 8.
# dnf -y install kernel-core
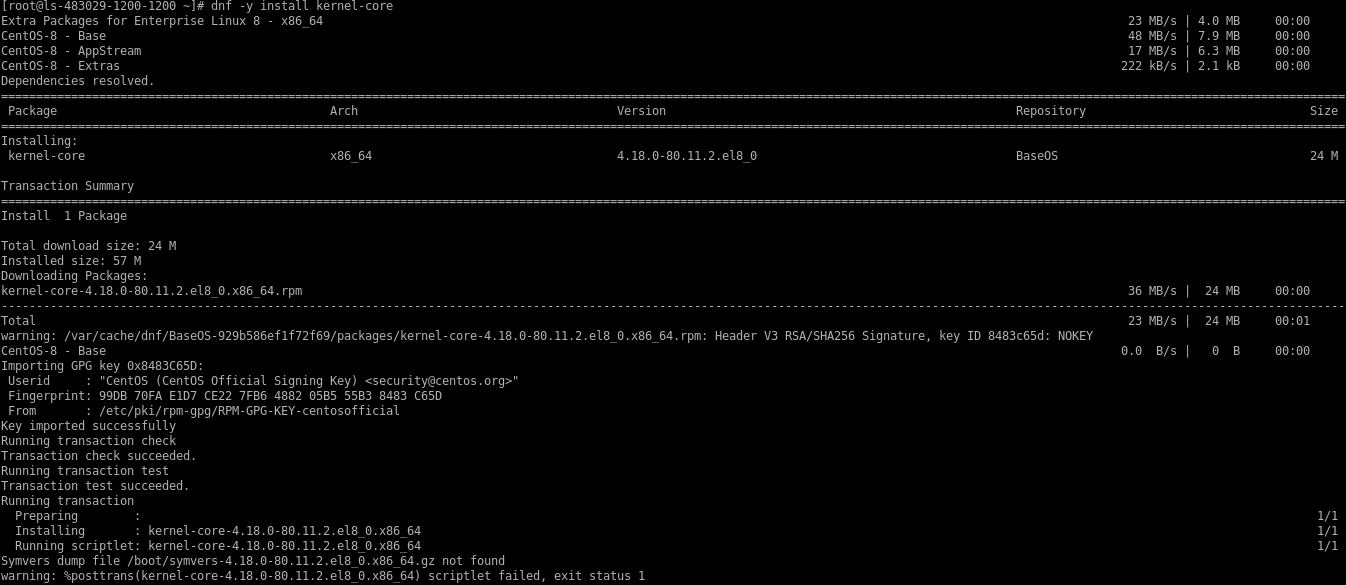
Install minimal package for CentOS 8.
# dnf -y groupupdate "Core" "Minimal Install"
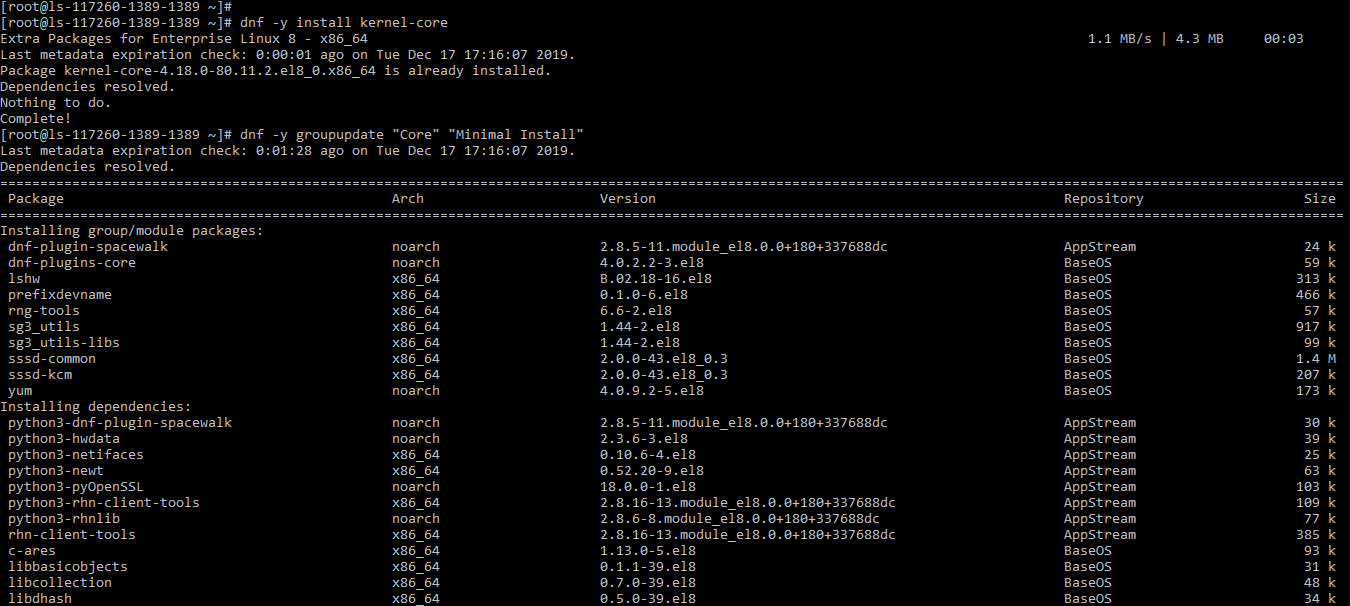
All the steps done. Now you can check the CentOS version in the server.
# cat /etc/redhat-release
