How to upgrade from Fedora 36 to Fedora 38
Fedora Linux, known for its cutting-edge features and robust security, regularly releases new versions to provide users with the latest software advancements. If currently using an older version of Fedora and wish to experience the latest features and improvements, upgrading to Fedora 38 is a great choice. This comprehensive guide walks through the process of upgrading the Fedora distribution using the DNF package manager.
Before beginning, it is essential to back up important data and configuration files to avoid any potential data loss during the upgrade process. While upgrades are generally safe, having a backup ensures quick recovery of files if needed.
Here's a detailed step-by-step guide for upgrading the Fedora distribution:
We are using Fedora Linux 36 (Server Edition) in our Cloud Servers:
Updating package information and refreshing repositories
On the Fedora system, enter the following command in the terminal:
# dnf upgrade --refresh -y
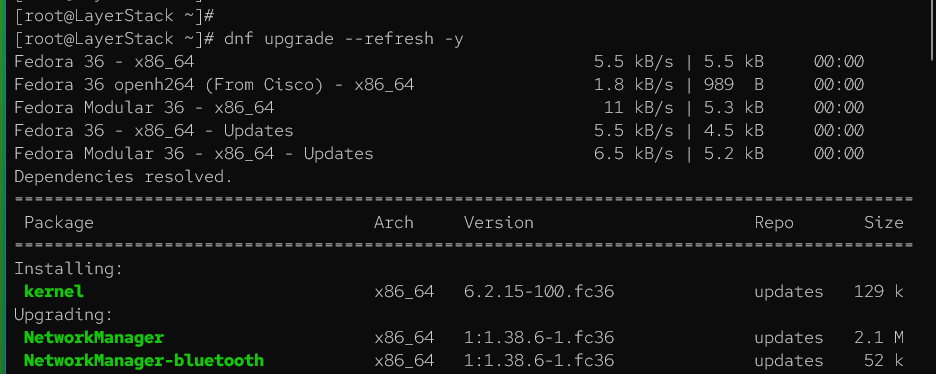
This command updates the package information and refreshes the repository metadata, ensuring having the latest package lists and dependencies before proceeding.
Installing the DNF system upgrade plugin
In some Fedora installations, the dnf-plugin-system-upgrade package might not be installed by default. To ensure having the necessary tools for system upgrading, execute the following command:
# dnf install dnf-plugin-system-upgrade
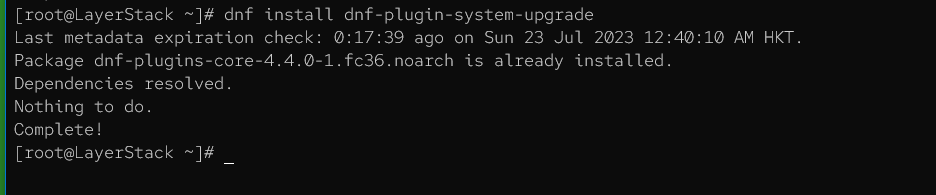
This will install the plugin that enables the system to upgrade functionality.
Downloading Fedora 38 packages
Download all the packages required for the upgrade to Fedora 38. Run the following command:
# dnf system-upgrade download --releasever=38 -y
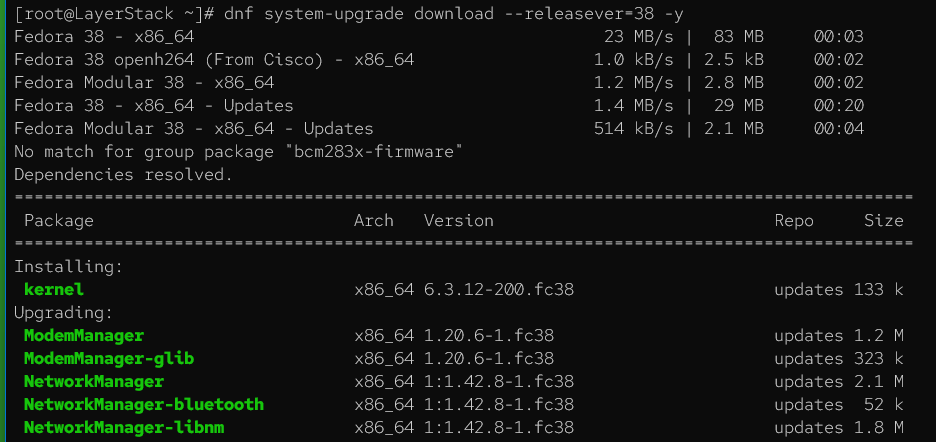
DNF will now download all the necessary packages from the Fedora 38 repositories. The time this step takes depends on the internet connection speed and the number of packages that need to be downloaded.
Performing the system upgrade and reboot
Once the packages are downloaded, it's time to initiate the system upgrade. Before proceeding, ensure all work is saved, and any important applications are closed.
To begin the upgrade process, run the following command:
# dnf system-upgrade reboot

This command will start the upgrade process and automatically reboot the system. During the reboot, the system will go through the upgrade process, and the packages will be installed. This can take some time, depending on the number of packages being upgraded.
To check the live progress, log in to the LayerPanel and click on Console option.

After the upgrade is completed, the system will be running Fedora Linux 38 (Server Edition).
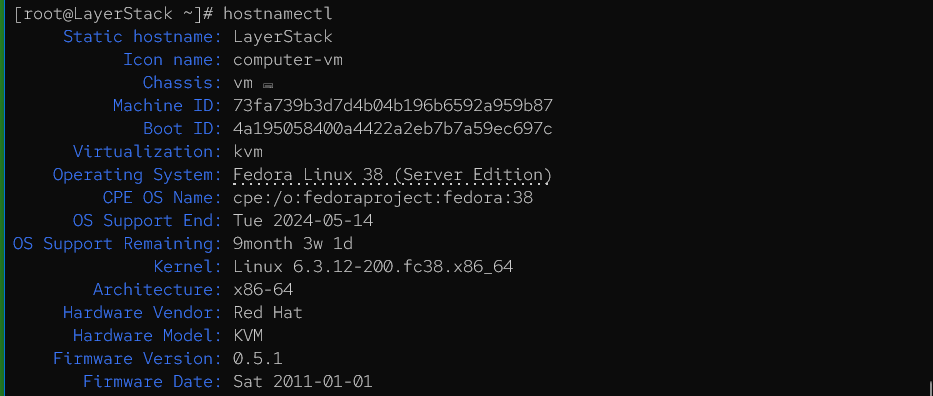
Completing the upgrade
After the reboot, the Fedora system should be running on version 38. However, there might be some additional tasks to complete, such as handling new configuration files or resolving potential issues with specific packages.
To finalize the upgrade, log in to the system and open the terminal again. Run the following command to ensure all packages are consistent and up to date:
# dnf distro-sync

This command will synchronize packages and dependencies to make sure everything is in order after the upgrade.
Cleaning up and removing old packages
After the upgrade, free up disk space by removing old, unnecessary packages from the previous Fedora version. Execute the following command:
# dnf autoremove -y
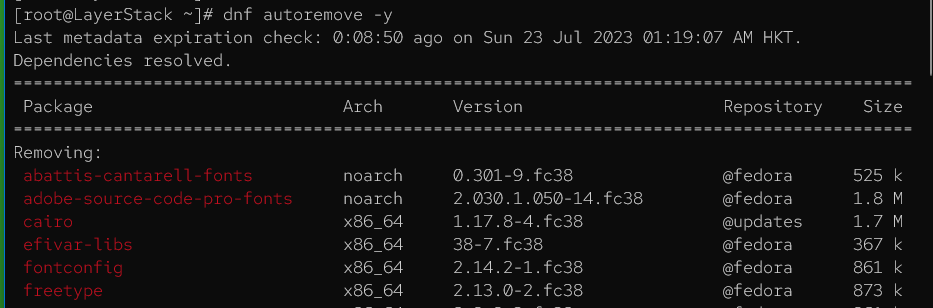
This will remove packages that are no longer needed on the system.
The Fedora system should now be upgraded to version 38. Verify that everything is working as expected and enjoy the new features and improvements of Fedora 38.
