How to use Object Storage on Linux Cloud Servers
LayerStack’s object storage is given a unique identifier and is stored in a flat memory model, it can enable users to store and retrieve any amount of data at any time or place, giving access to highly scalable, fast, reliable, and inexpensive data storage. It can also be easily optimizable, organizable and configurable to support a wide range of organizational, Business and compliance-specific data management requirements.
To deploy Object storage service and create Bucket
Log in to LayerPanel2 (https://cp.layerpanel.com/) account and select the
Services>>Object storageas in the below screenshot.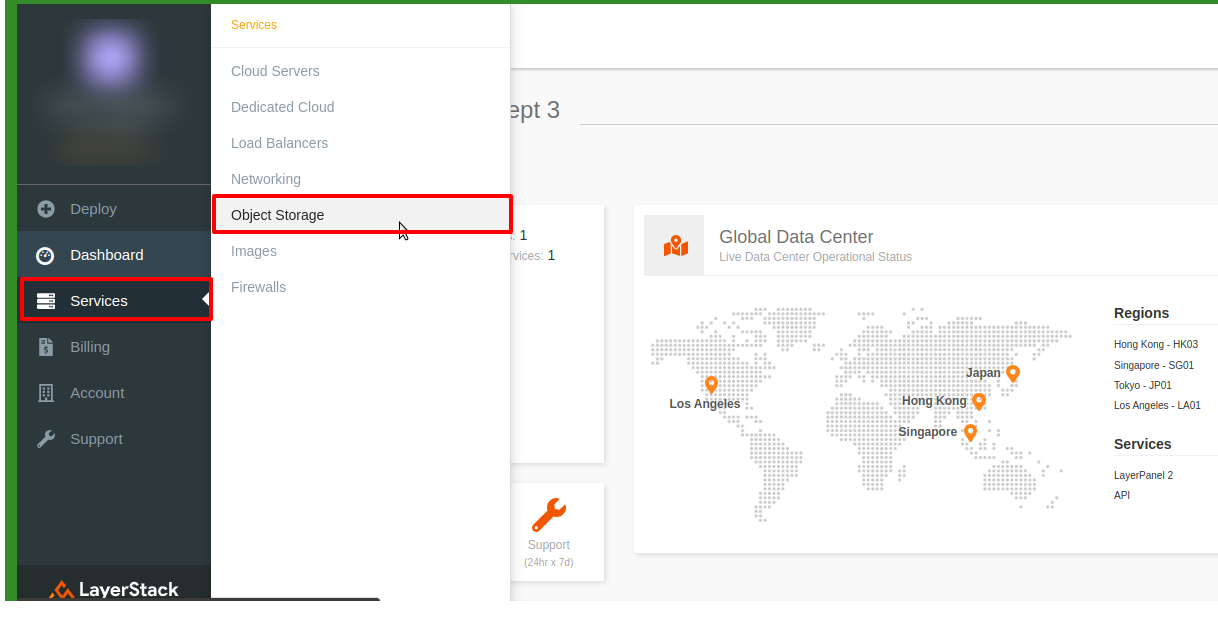
Deploy an Object Storage in a region, you would be able to create
bucket storagein either Hong Kong or Singapore.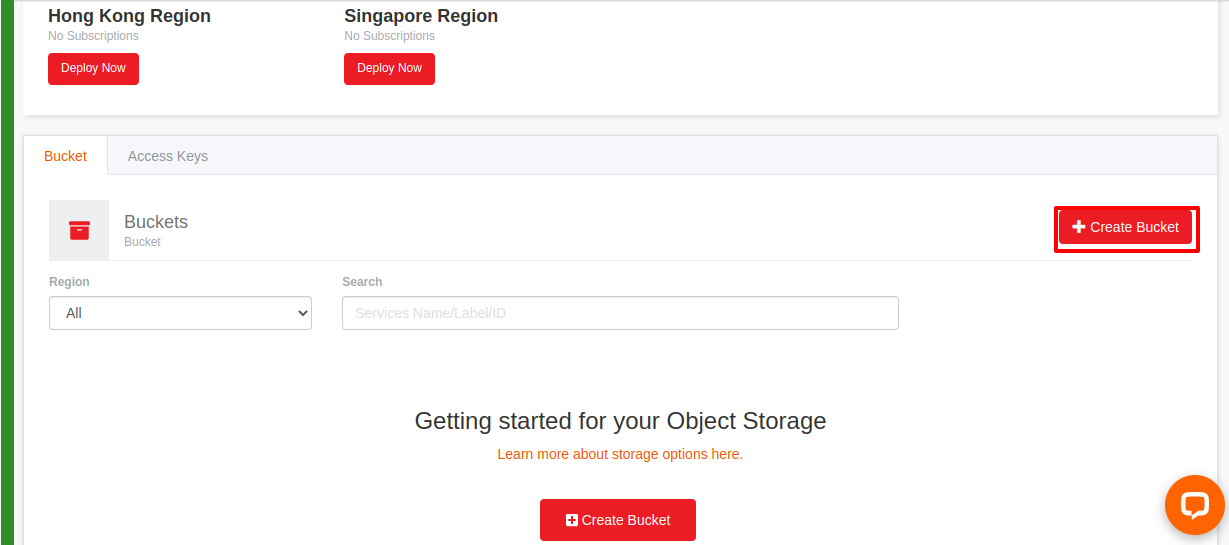
Go ahead and pay up the order generated and then come back to the Object storage page.
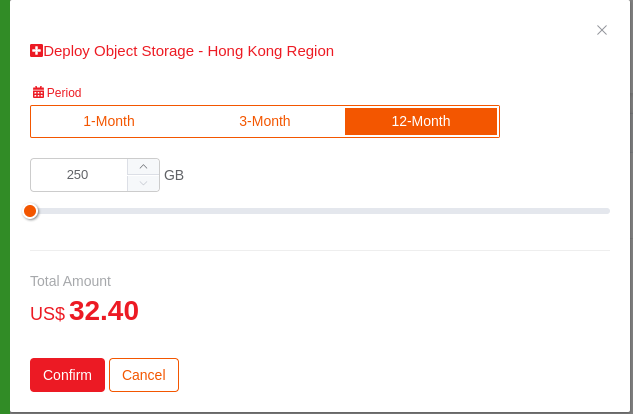
Once done, you would be able to click on
Create BucketButton.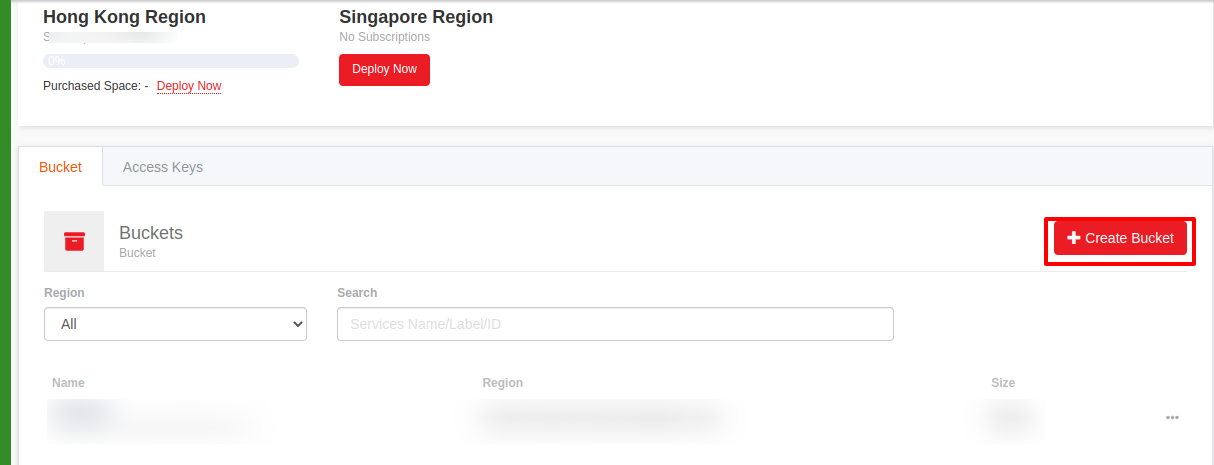
Enter the
bucket nameandregionof preference.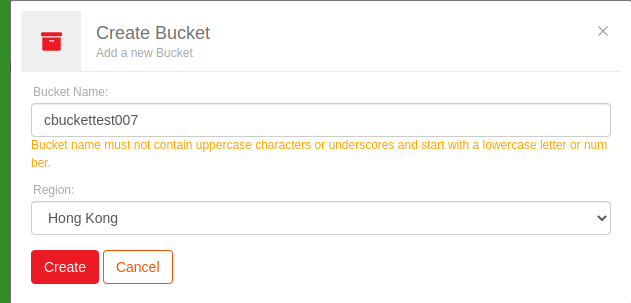
Once done you would be able to view the created bucket listed.
To configure and mount the service to the Cloud Servers
In order to make use of the Object Storage service, involves both configuring the service and mounting the service to the server. Configuration is done using the s3cmd command and mounting is performed using the s3fs command.
s3cmd is a tool to manage buckets and files and you may refer to the following steps in order to install s3cmd on Linux servers.
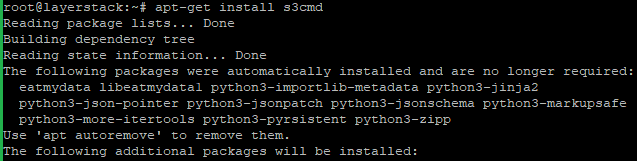
Ubuntu/Debian:
# apt-get install s3cmd
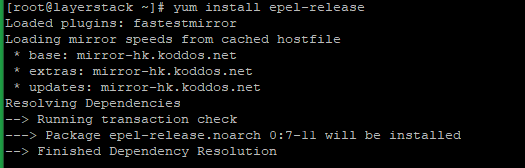
CentOS/RHEL and Fedora:
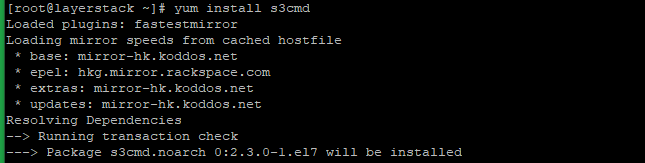
# yum install epel-release
# yum install s3cmd
The below steps can be followed to configure the Object Storage service in the server using s3cmd:
Log in to the Linux server by using SSH.
Input the following command.
# s3cmd --configureInput your
Access KeyandSecret Key, both keys can be found from your LayerPanel service's page.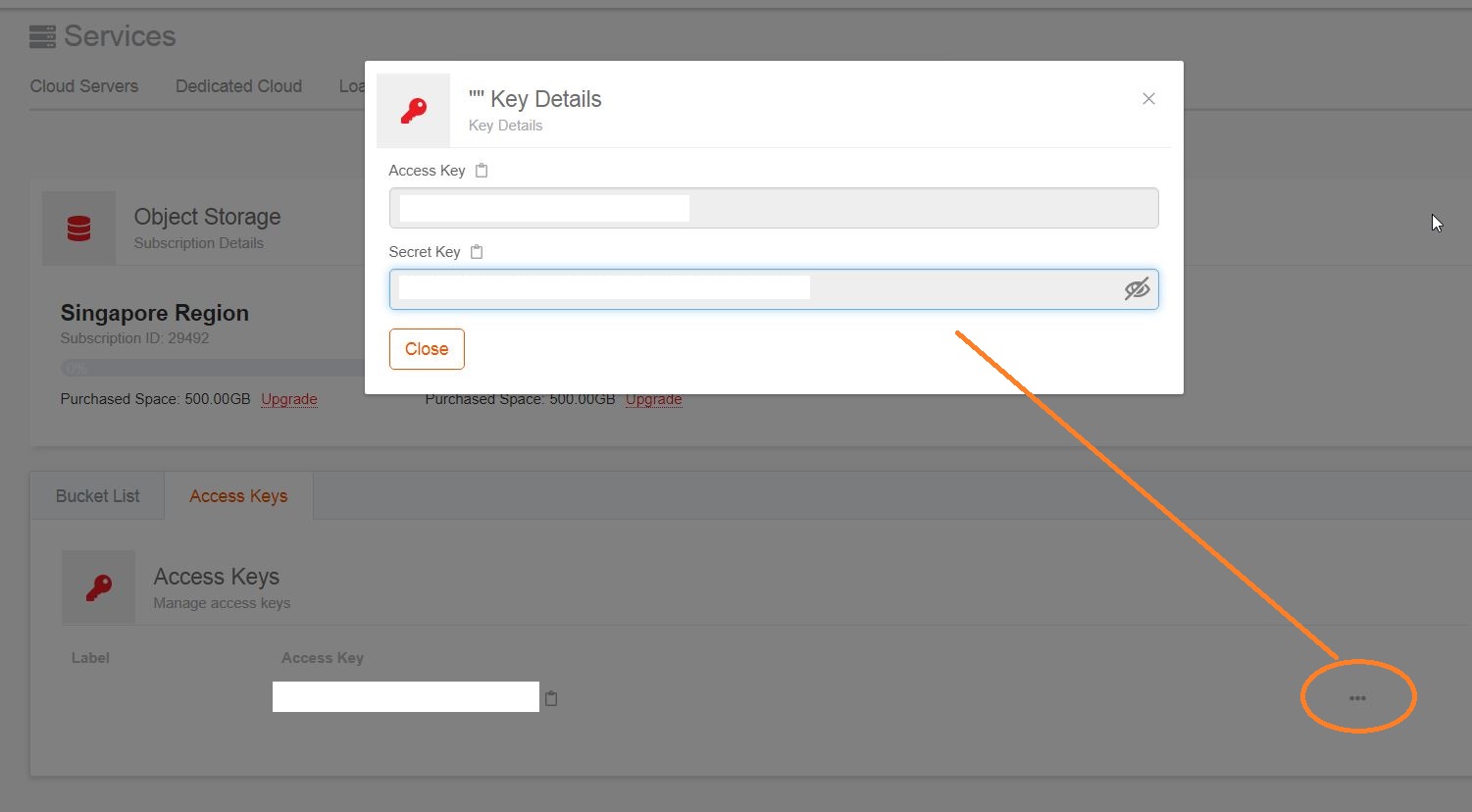
Input your location for
Default Region.Specify
hks3.layerstackobjects.comfor the HK region orsgs3.layerstackobjects.comfor the SG region forS3 Endpoint.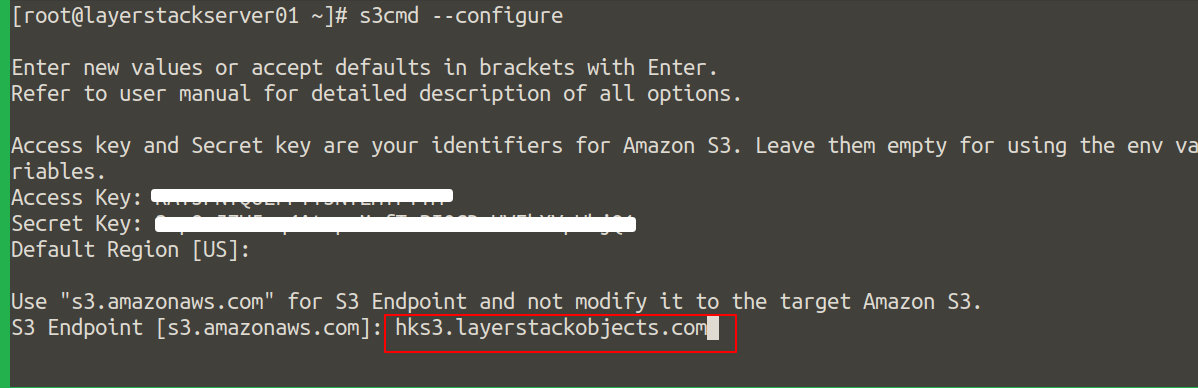
Specify
noforDNS-style bucket+hostname:port template for accessing a bucket.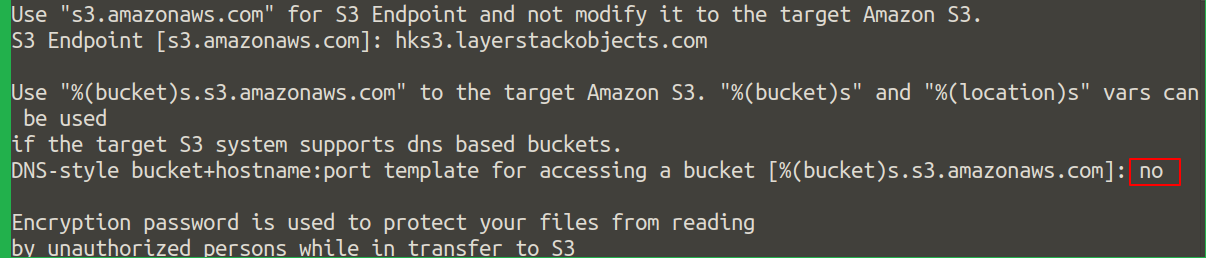
Specify a password of your choice for
Encryption passwordif necessary.Press return for
Path to GPG programif necessary.Press return for
Use HTTPS protocolif necessary.Press return for
HTTP Proxy server nameif necessary.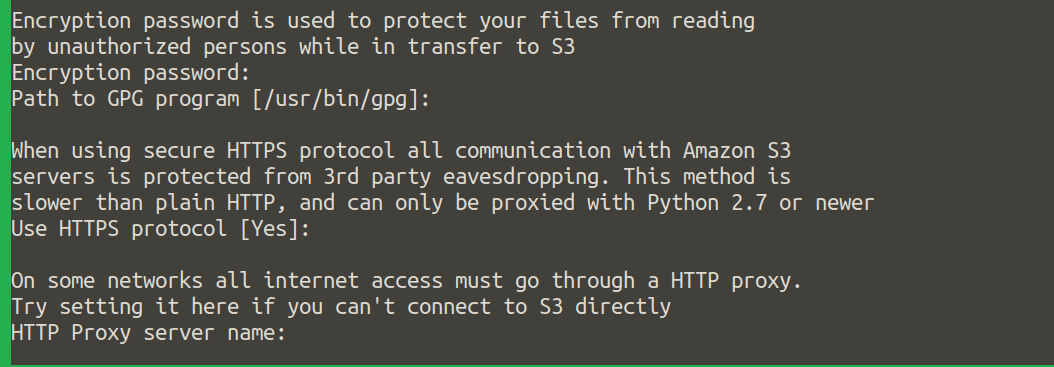
Confirm by specifying
y.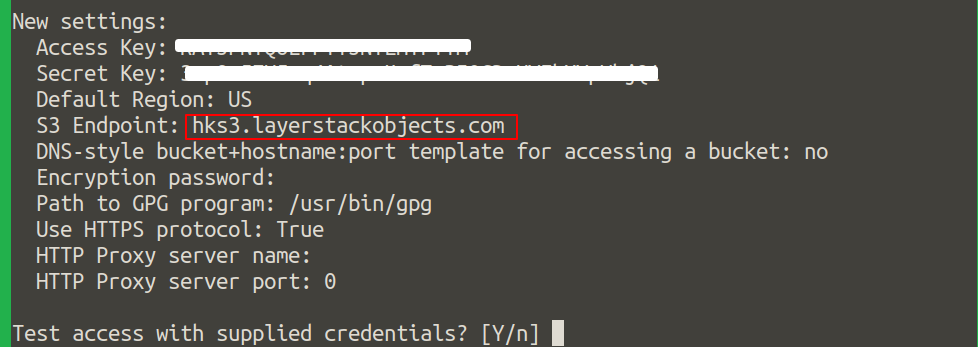
Confirm again by specifying
y.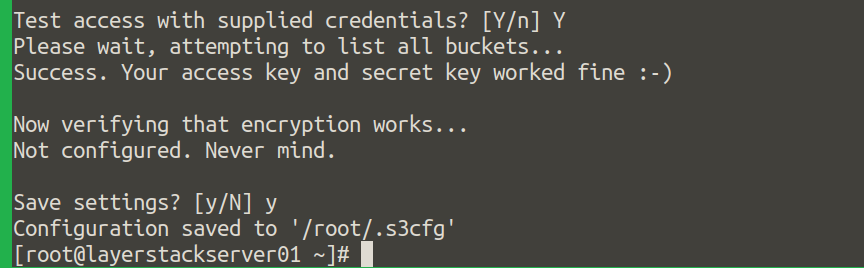
FUSE is also useful for users who want to access the data stored in the same way they would access a local file system. It provides a way to mount an S3 bucket so that it can be used as part of a local file system.
s3fs allows Linux, macOS, and FreeBSD to mount an S3 bucket via FUSE to the Cloud server.
S3fs mounts an S3 bucket as a local file system. The API implementation supports directory operations like create, delete, move, etc. along with basic file operations like read, write, delete, etc. This tutorial will help you to mount the S3 object storage to the Cloud Servers.
Installation of s3fs-fuse is the prerequisite for this tutorial. As the utility can be installed on all Linux OS as well as Mac OS. You may refer to the following steps to install s3fs-fuse in Linux servers.
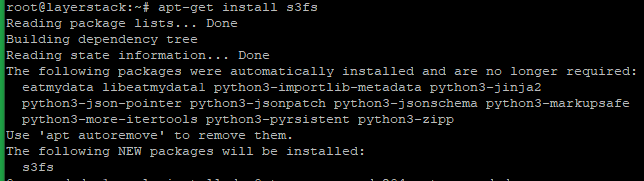
Ubuntu/Debian:
# apt-get install s3fs
CentOS/RHEL and Fedora:
# yum install epel-release
# yum install s3fs-fuse
Once S3fs FUSE is installed, the below steps can be followed for mounting the object storage.
A setting file needs to be created using the Access key and secret key with the format.
Access_key : Secret_key echo access_key:secret_key > ${HOME}/.passwd-s3fs
Set the permissions accordingly to secure the file.
# chmod 600 ${HOME}/.passwd-s3fs
Create a new folder which is the mount point for the Object storage.
# mkdir ${HOME}/<bucket-name>
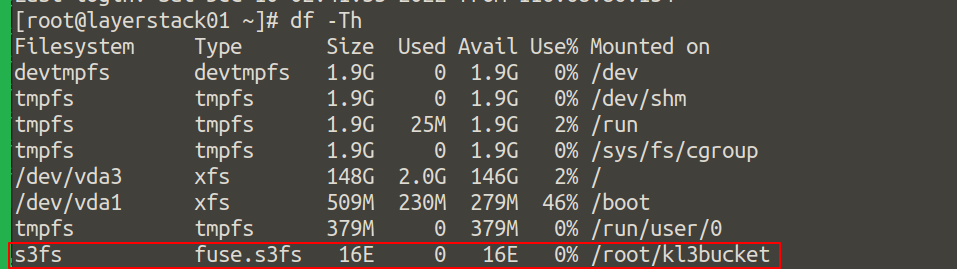
Now, the bucket is mounted on the mounting point.
# s3fs <bucket-name> ${HOME}/<bucket-name> -o passwd_file=${HOME}/.passwd-s3fs -o url=https:// [hks3.layerstackobjects.com](http://hks3.layerstackobjects.com/) -o use_path_request_style
NOTE: Please use
sgs3.layerstackobjects.comfor the SG region.Finally, you would be able to view the mount point.