sudo permits an allowed user to execute a command as the superuser or another user, as determined in the sudoers document. Setting the original and effective UID and GID to match the target user specified in the passwd file and initializing the group vector based on the group file.
This is a great way to avoid security issues and it requires users to authenticate with passwords by default.
This article will guide you to the basic commands about using sudo or sudoers to start, stop & restart Apache on a common Linux OS.
CentOS / Fedora
Below are the normal commands to start, stop and restart the Apache with sudo.
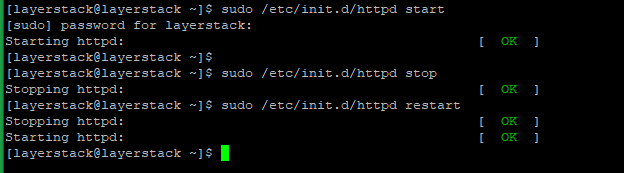
# sudo /etc/init.d/httpd start
# sudo /etc/init.d/httpd stop
# sudo /etc/init.d/httpd restart
The below error will get while trying to run the above-mentioned commands without editing the sudoers file.
**layerstack** is not in the sudoers file. This incident will be reported.

Here layerstack is a standard user that using for giving permission to start/stop/restart Apache Web Server.
Now open /etc/sudoers file with any text editor and add the below line.
# vi /etc/sudoers

layerstack ALL = /etc/init.d/httpd
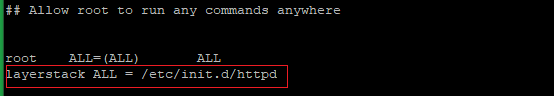
Note: Replace the username layerstack with your original username.
Save the file by pressing,
:w! and then Enter
Now can start, stop and restart the Apache with sudo by using the commands mentioned earlier and using the password of the user while proceeding with these.
Ubuntu / Debian
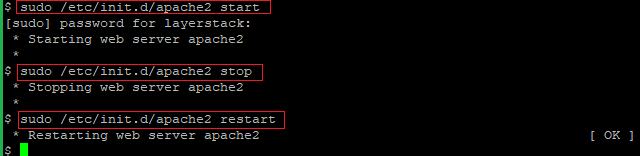
Below are the commands to start, stop and restart the Apache with sudo.
# sudo /etc/init.d/apache2 start
# sudo /etc/init.d/apache2 stop
# sudo /etc/init.d/apache2 restart
The below error will get while trying to run the above-mentioned commands without editing the sudoers file.
**layerstack** is not in the sudoers file. This incident will be reported.
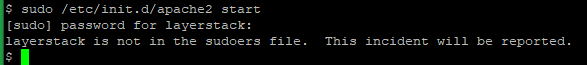
Here layerstack is a standard user that using for giving permission to start/stop/restart Apache Web Server.
Now open /etc/sudoers file with any text editor and add the below line.
# vi /etc/sudoers

layerstack ALL = /etc/init.d/apache2
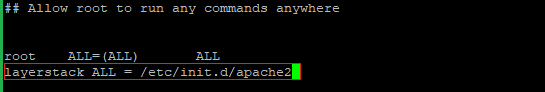
Note: Replace the username layerstack with your original username.
Save the file by pressing,
:w! and then Enter
Now can start, stop and restart the Apache from the user with sudo by using the commands mentioned earlier and using the password of the user while proceeding with these.
Related Tutorials