Ping (ICMP Echo Requests) is a fundamental tool for diagnosing network connectivity issues. It helps determine whether a server is reachable and measures the response time. However, due to security concerns, Ping requests are often blocked by the Windows Server firewall by default. Enabling Ping allows administrators to troubleshoot network problems efficiently, while disabling it enhances security by preventing potential attacks.
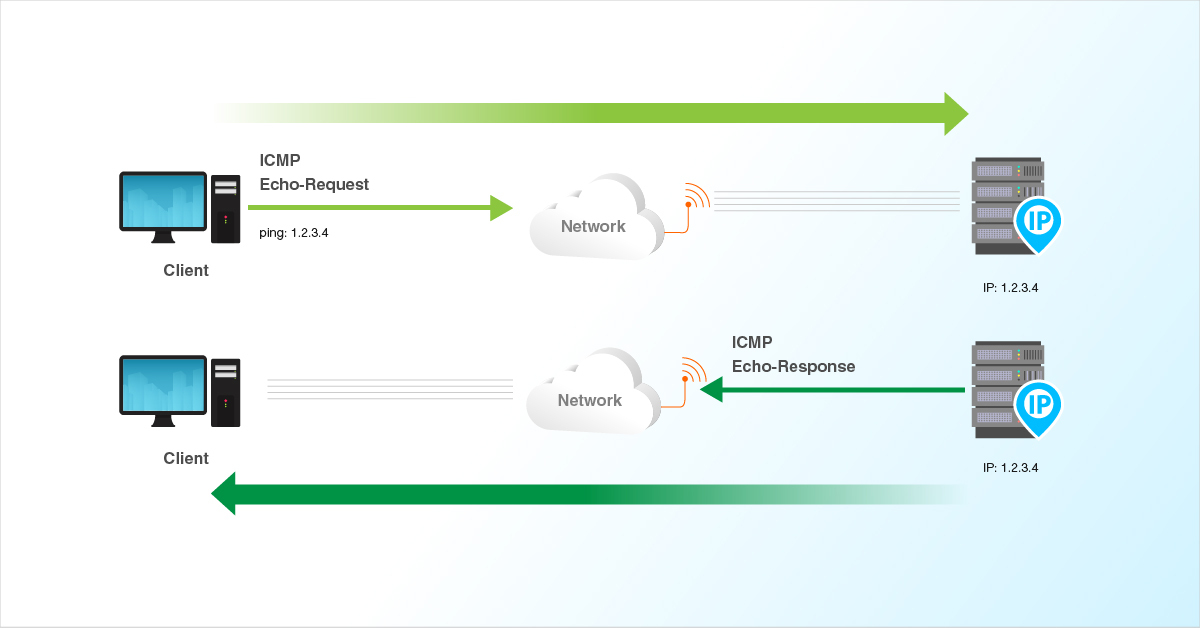
This guide provides clear, step-by-step instructions to enable and disable Ping (ICMP Echo Requests) in Windows Server 2025.
To Enable Ping for IPv4
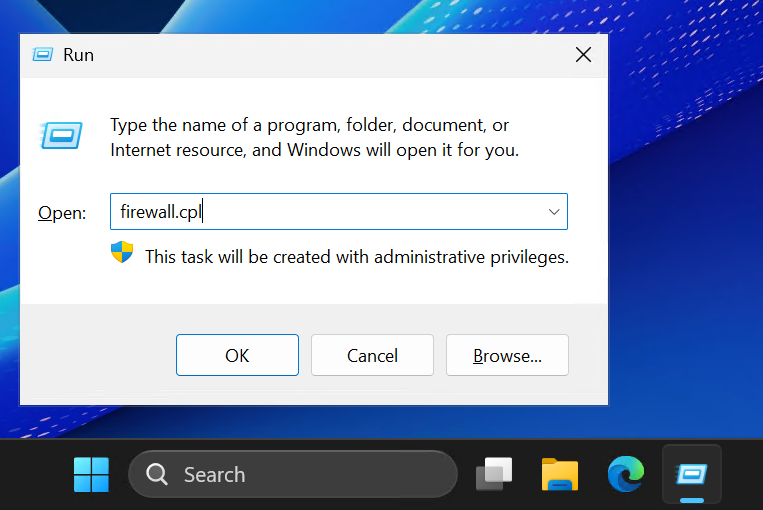
Open the Windows Firewall settings.
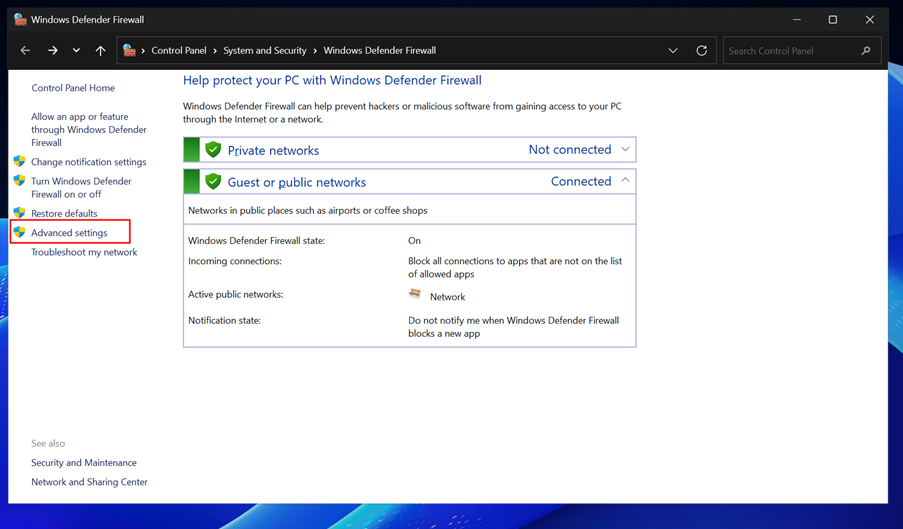
Click on Advanced settings in the left-hand menu and can see the Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security window.
Navigate to Inbound Rules on the left panel.
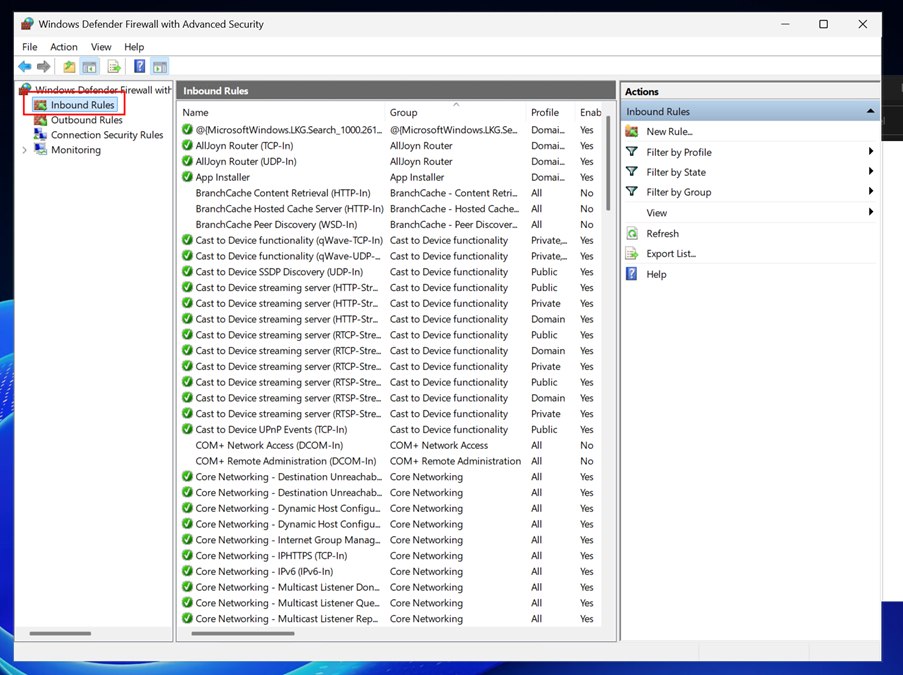
Locate the rule named File and Printer Sharing (Echo Request - ICMPv4-In) in the list.
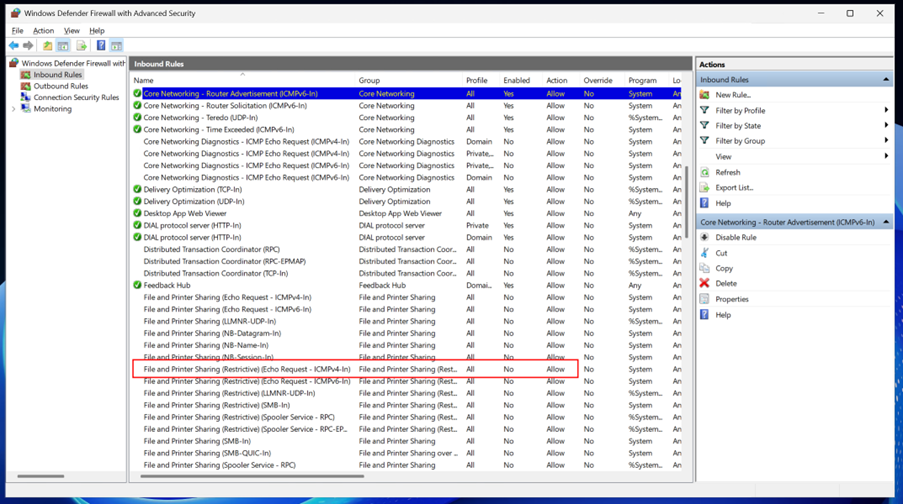
Right-click the rule and select Enable Rule. This allows incoming ICMP Echo Requests (Ping) for IPv4.
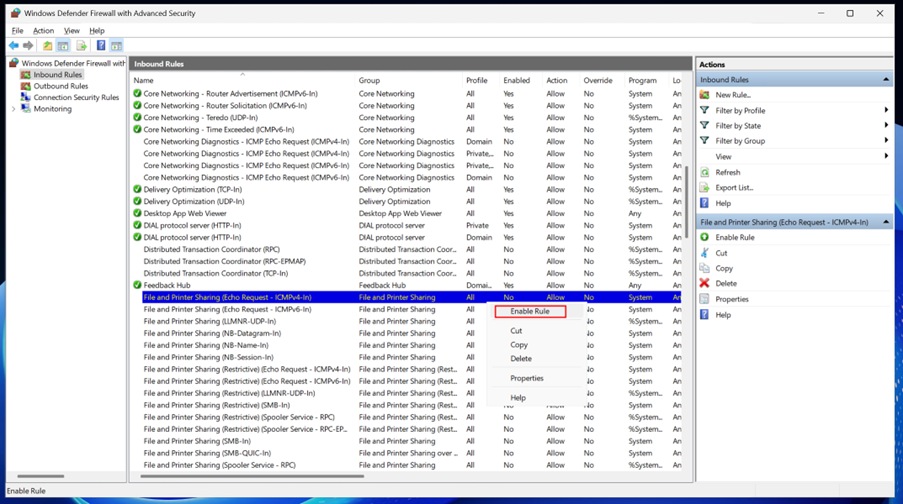
Close the firewall settings.
Verify that Ping is enabled by opening the Command Prompt (cmd) and running the following command:
# ping <server-ip>
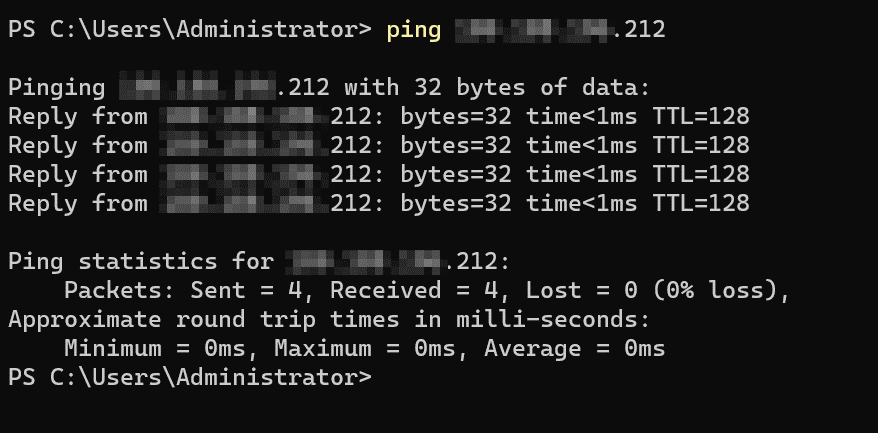
If Ping is enabled, you should receive responses from the server.
To Enable Ping for IPv6
Follow steps 1–3 from the IPv4 section.
Locate File and Printer Sharing (Echo Request - ICMPv6-In) under Inbound Rules.
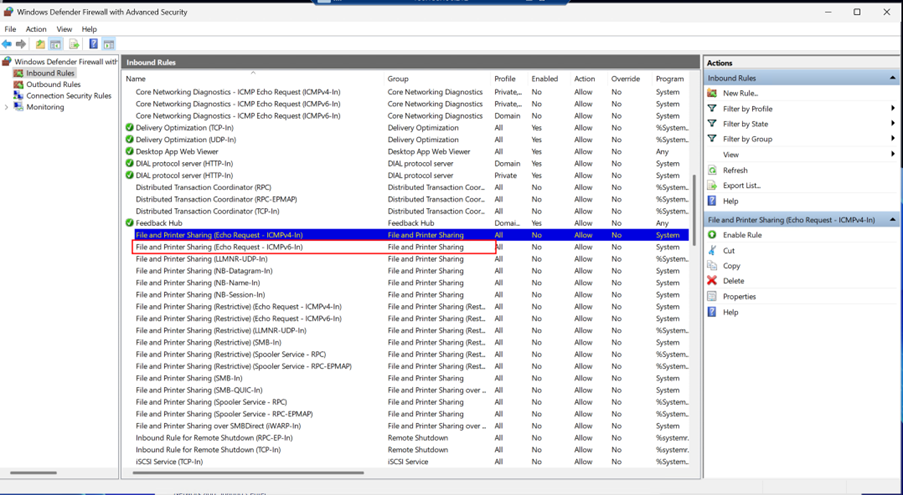
Right-click the rule and select Enable Rule.
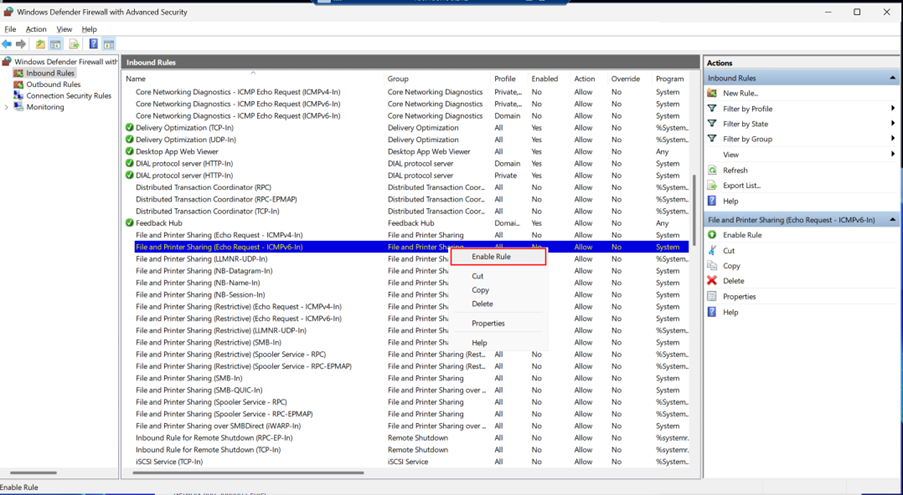
Close the firewall settings and verify IPv6 Ping using:
# ping -6 <server-ip>
To disable Ping for IPv4
Follow steps 1–4 from the IPv4 section.
Locate File and Printer Sharing (Echo Request - ICMPv4-In) and Right-click the rule and select Disable Rule.
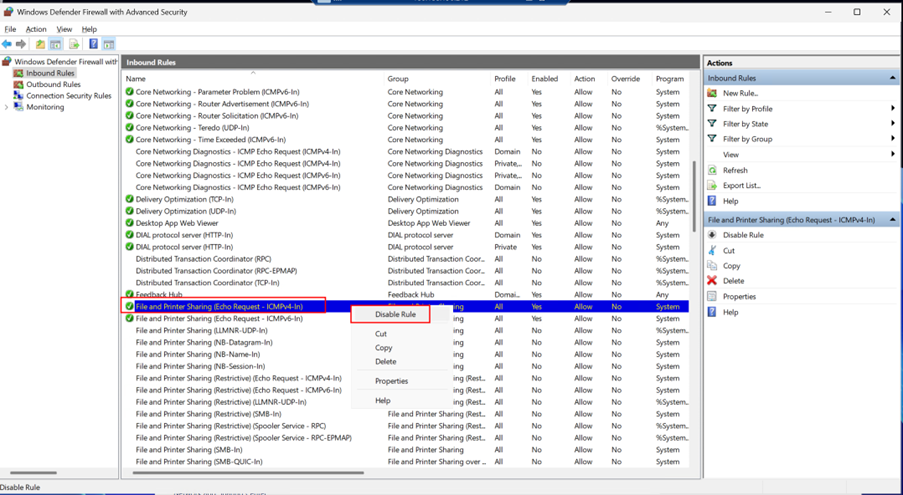
Close the firewall settings.
To disable Ping for IPv6
Follow steps 1–4 from the IPv4 section.
Locate File and Printer Sharing (Echo Request - ICMPv6-In) under Inbound Rules and Right-click the rule and select Disable Rule.
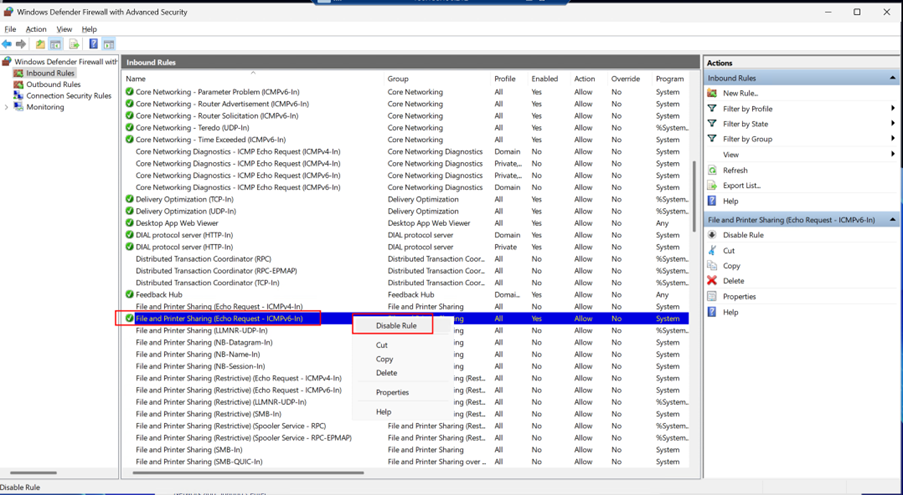
Close the firewall settings.
By following these steps, you can control ICMP Echo Requests (Ping) functionality on your Windows Server 2025, enabling or disabling it based on your security and troubleshooting needs.
Related Tutorials