In just five months, Mr. Jensen Huang, the founder of Nvidia, has experienced a surge of net worth by 146% reaching around $20.2 billion. This positioned him as the 37th richest person in the world and established him as the fastest-growing billionaire on the wealth rankings this year.
Following the release of Nvidia’s first-quarter earnings report earlier, the company witnessed a price rose by 28% in just one day, resulting in a market value of approximately $755.2 billion. Some experts even suggest that Nvidia might become the world’s first trillion-dollar chip company.
Nvidia’s Key Innovations

Among the numerous inventions credited to Nvidia, two stand out as monumental contributions to the world of computing. These innovations have had a profound impact on the industry and continue to shape its trajectory.
The GPU: Nvidia holds the distinction of being the pioneer behind the creation of the world’s first graphics processing unit (GPU). The importance of GPUs in the past couple of decades cannot be overstated. They have enabled advancements in machine learning, video editing, and modern gaming software, fueling technological progress across various fields.
The Omniverse: Looking toward the future, Nvidia’s Omniverse emerges as a potentially transformative invention. Serving as a real-time reference platform and tool, the Omniverse empowers developers and designers to render, simulate, and create scalable 3D simulations. It has the potential to form the foundation of the virtual world that many envision.
Nvidia’s GPUs have become the new driving force in the AI field, potentially replacing Apple as Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company’s (TSMC) main influencer. This multinational tech company is now considered one of the most important in the world, yet you might not even know half of what the company does, where it came from, and what it’s responsible for bringing to the tech world at large. Let’s take a closer look at the facts surrounding Nvidia below.
The Real Game Changer

The journey of Nvidia began in the 1990s. With a modest sum of $40,000 pooled together, the three co-founders Jensen Huang, Chris Malachowsky, and Curtis Preim established the company named Nvidia, which is a fusion of “new version” and the Latin word for envy, “invidia.”
Their research and exploration into graphics-based computing, particularly in the context of video games, attracted the attention of venture capitalists who recognized the immense possibilities. The trio then secured a substantial $20 million in funding and made its public debut on January 22nd, 1999, marking the beginning of an extraordinary journey that would shape the technology landscape.
Nvidia’s Evolution Over the Decades
The success of the RIVA TNT and GeForce 256 paved the way for Nvidia to secure a contract with Microsoft for the graphics hardware of their Xbox gaming console. This contract alone earned Nvidia a substantial $200 million in advances. Despite the challenges of managing such a significant undertaking, Nvidia delivered an exceptional product to Microsoft while also developing their own GeForce 2 GTS.
Later they secured another significant contract, this time with Sony for the graphics hardware of the PlayStation 3, further strengthening their position in the gaming industry. However, the latter half of the decade was not without its challenges. Nvidia faced reports of defective GPUs and mobile phone chips, causing a significant setback for the company and its stock value.
At the beginning of the new decade, Nvidia resolved legal issues related to the faulty GPUs and mobile chips. They also struck a multi-billion-dollar deal with Intel, propelling them further forward. With a focus on automotive electronics, mobile devices, and video gaming, Nvidia continued to innovate and expand its offerings.
In the early 2010s, Nvidia introduced groundbreaking products such as the Tegra 3 ARM system-on-a-chip, the Tegra 4, and the Nvidia Shield—a handheld gaming console. They refined their strategy, tailoring releases to specific markets.
Notably, the launch of the GeForce 10 series in 2016 showcased Nvidia’s commitment to pushing technological boundaries. These graphics cards boasted impressive features, including simultaneous multi-projection (SMP) support, designed to enhance multi-monitor and virtual reality setups.
Despite a minor setback in 2016 with a lawsuit related to false advertising regarding the GTX 970’s RAM capabilities, Nvidia forged key partnerships with industry giants. Their artificial intelligence arm collaborated with Toyota and popular search engine Baidu, followed by partnerships with Google and Apple. By the end of 2019, Nvidia’s stock began an upward ascent, setting the stage for a promising future in the 2020s.
Nvidia in the Cloud
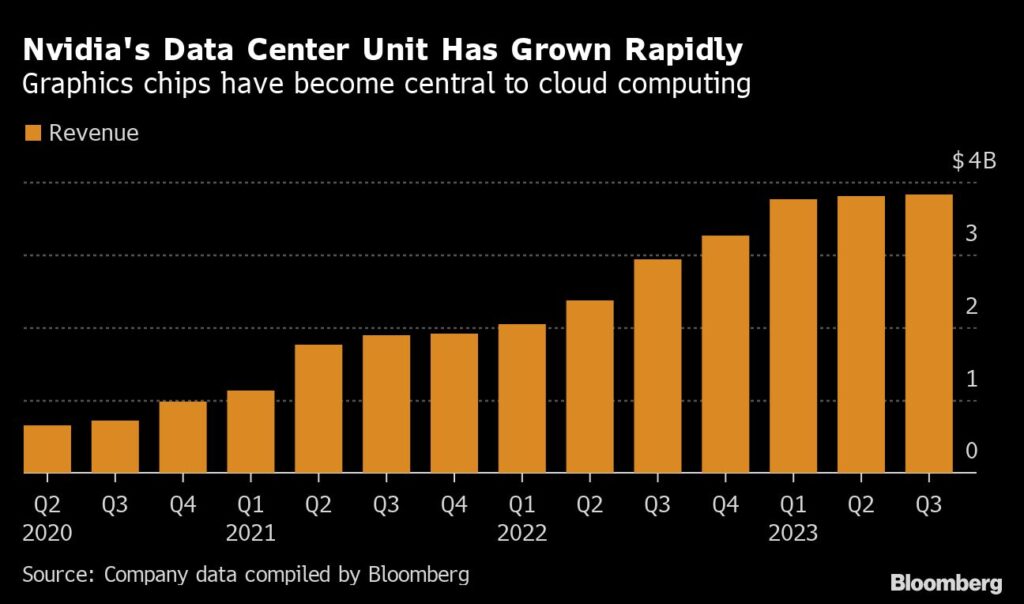
Undoubtfully, Generative Artificial Intelligence (AI) is now having a moment, with nearly every technology company hurrying to incorporate large language models into their offerings. NVIDIA lives at the center of this revolution, in which it spent the past two decades strategically investing in enabling enterprise AI.
It takes a lot of resources to handle even inference tasks for Generative AI, making it cost-prohibitive for smaller companies, and leading to large CapEx spend for enterprises. This is where the cloud makes sense.
The market is responding to the cloud-driven AI model. Almost every cloud service provider (CSP) is offering accelerated instances based on NVIDIA products, with Nvidia GPUs accounting for over 93% of GPU-accelerated instance types in the public cloud.

From its humble beginnings as a visionary venture exploring graphics-based computing, Nvidia has grown into a global powerhouse, leaving an indelible mark on the technology landscape.
With its groundbreaking GPUs, strategic partnerships, and commitment to pushing boundaries, Nvidia is poised to shape the future of computing, unlocking new possibilities and revolutionizing industries along the way.


