How to configure Global Private Networking for Cloud Servers
The private IP address with dedicated VLAN is provided for internal use behind a router and apart from the public internet. This allows you to add a second interface (E.g. ETH1) to your Cloud Servers with a range of private IPs (E.g. 172.16.0.0/16) that is not publicly accessible.
Mostly, it is used for communicating with a group of other servers in the same network. Also, the public cannot check the traffic of private networking anywhere and this, in turn, improves the server privacy.
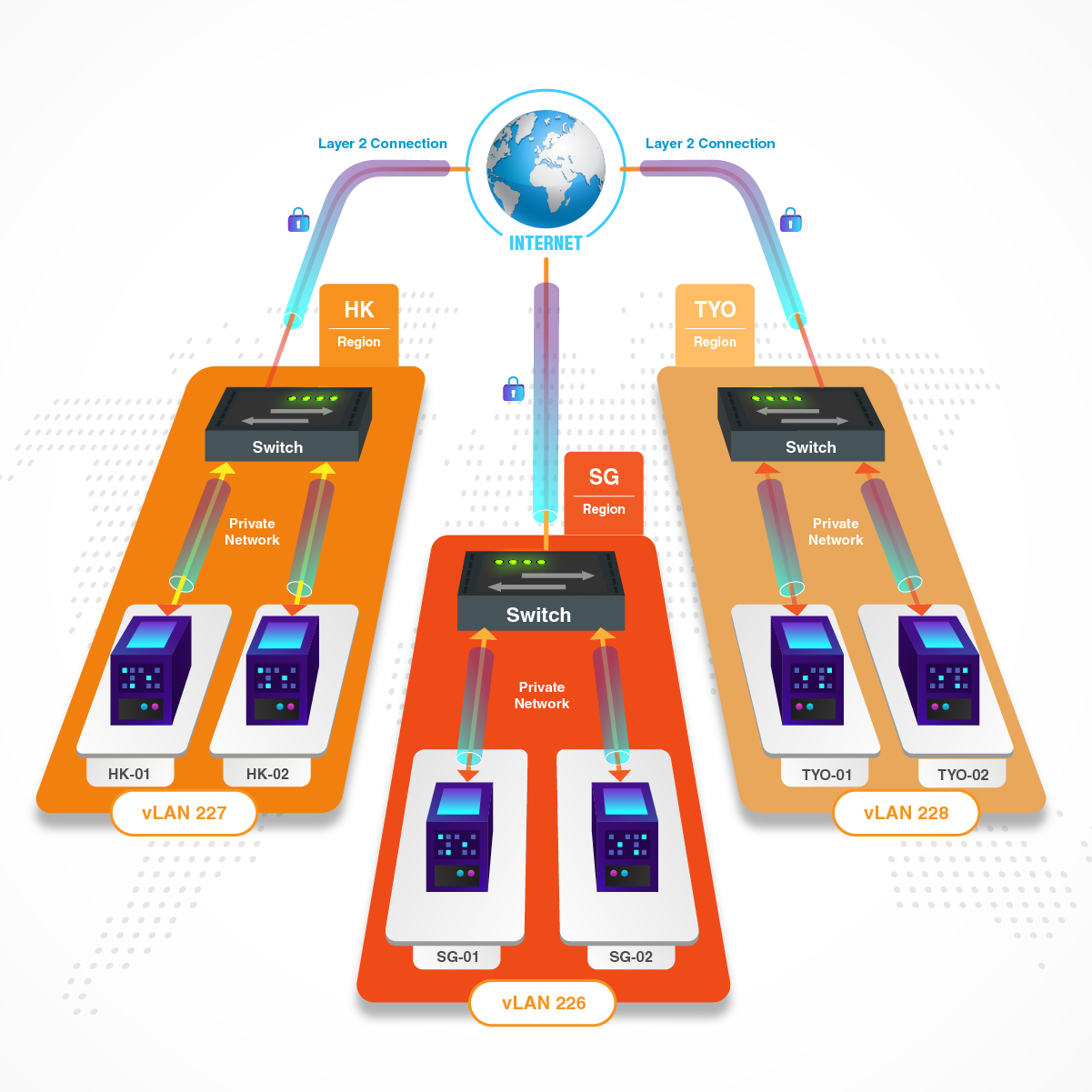
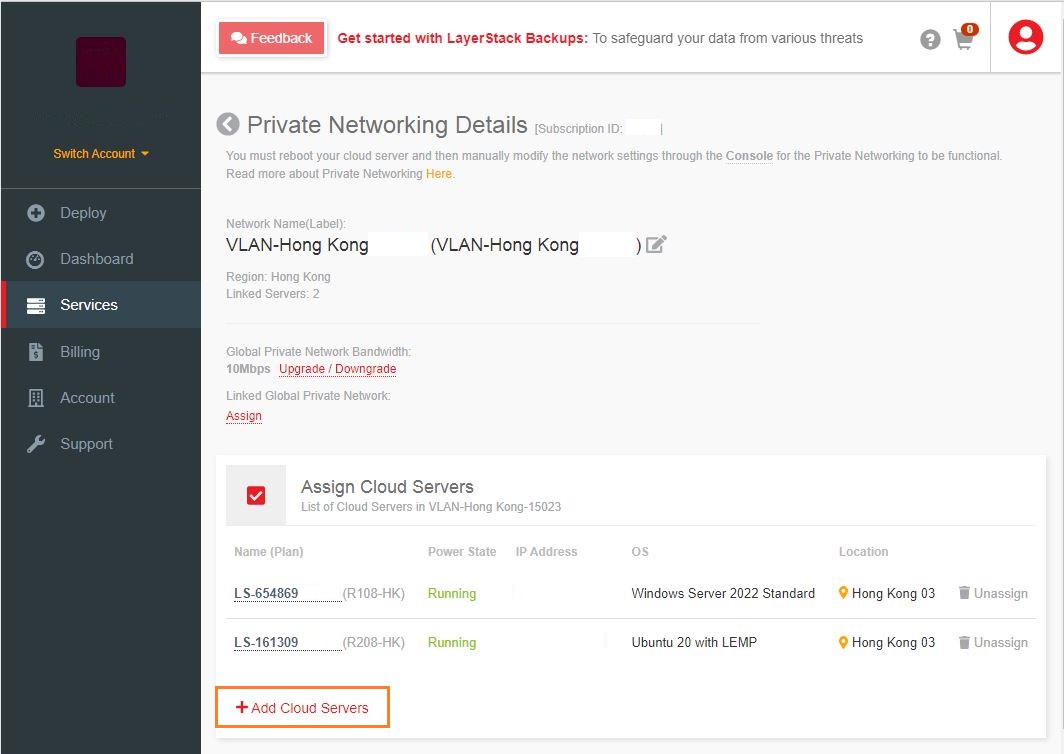
You can assign several required Cloud Servers into one VLAN under the Private Networking section of LayerPanel first, this can allow VMs under the same region to communicate through local private networking.
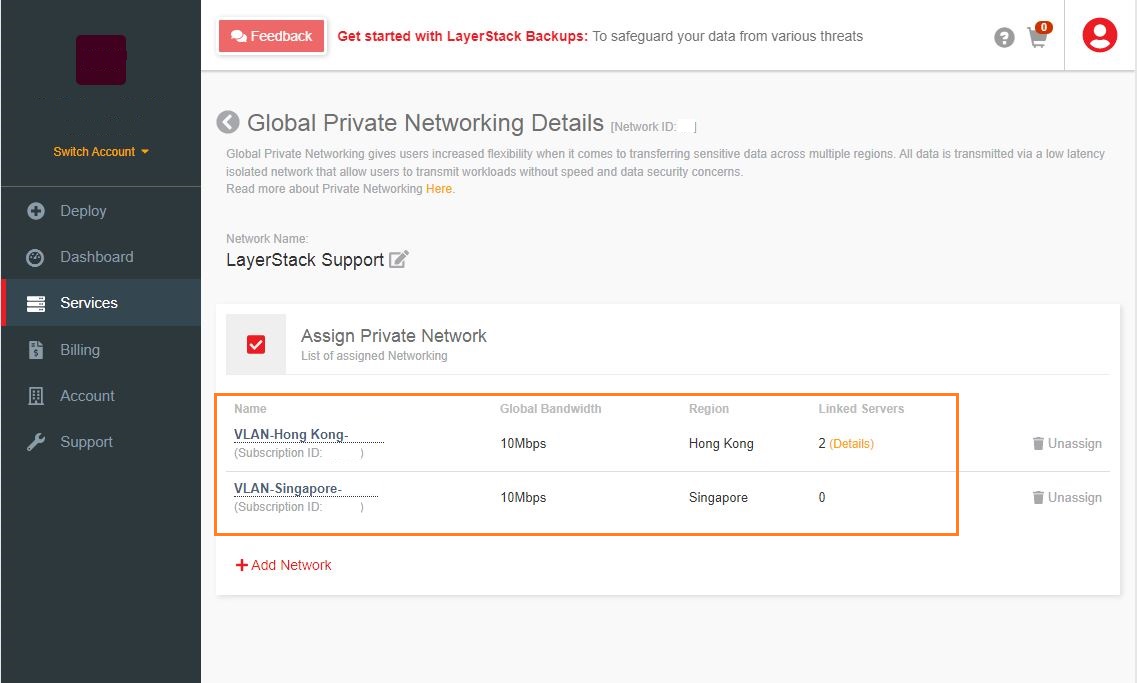
For using Global private networking, assign the available VLAN from different regions (E.g. Hong Kong, Singapore) into this global connection as follows.
After that, you may see the instructions for configuring the private IP address for Windows OS, AlmaLinux, RockyLinux, CentOS, Debian, Ubuntu & Fedora below.
Windows OS
Click
Start Menu, then clickControl Paneloption.Click
Network & Sharing Centeroption.Click
Change adapter settingsin the left panel.Right-click adapter with the name
Ethernet 2and selectProperties.In the properties window, select
Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)and clickPropertiesbutton.Select
Use the following IP address:option and configure the private IP address.
The following IP ranges are required to use as private IP addresses:
10.0.0.0/8
172.16.0.0/16
192.168.0.0/24
Example for 172.16.3.123:
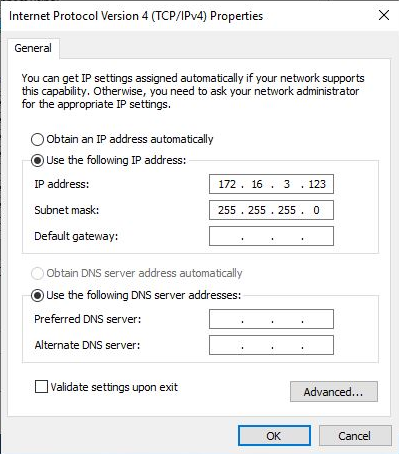
Note: The netmask of LayerStack private IP range is /24 subnet (255.255.255.0).
Once IP and Subnet are entered check the box
Validate Settings upon exit, clickOKand then close theEthernet 2 propertywindow.Windows Network Diagnostic toolwill run to check to see any issues, close this window.To check if the private IP address is configured properly, right-click
Start Menu, then clickCommand Prompt.Execute the following command for checking network configuration.
# ipconfig
AlmaLinux
Edit the network configuration file using the below command.
# vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ens7
Note: ens7 is the device name of the server. Please replace with the correct device name if necessary.
Add the following entries for the network card and configure the preferred private IP address.
The following IP ranges are required to use as private IP addresses:
10.0.0.0/8
172.16.0.0/16
192.168.0.0/24
Example for 172.16.3.123:
DEVICE=ens7 ONBOOT=yes BOOTPROTO=static IPADDR=172.16.3.123 NETMASK=255.255.255.0 USERCTL=no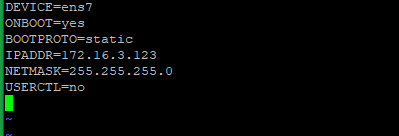
Note: The netmask of LayerStack private IP range is /24 subnet (255.255.255.0).
Save the file.
Restart the network service and make the changes effect.
# systemctl restart NetworkManager.serviceCheck the private IP address configured properly inside the network card.
# ifconfig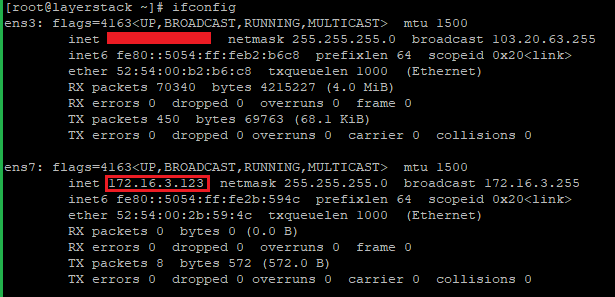
RockyLinux
Edit the network configuration file using the below command.
# vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ens7
Note: ens7 is the device name of the server. Please replace with the correct device name if necessary.
Add the following entries for the network card and configure the preferred private IP address.
The following IP ranges are required to use as private IP addresses:
10.0.0.0/8
172.16.0.0/16
192.168.0.0/24
Example for 172.16.3.123:
DEVICE=ens7 ONBOOT=yes BOOTPROTO=static IPADDR=172.16.3.123 NETMASK=255.255.255.0 USERCTL=no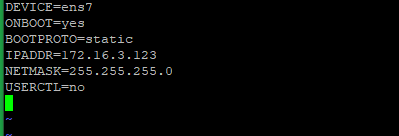
Note: The netmask of LayerStack private IP range is /24 subnet (255.255.255.0).
Save the file.
Restart the network service and make the changes effect.
# systemctl restart NetworkManager.serviceCheck the private IP address configured properly inside the network card.
# ifconfig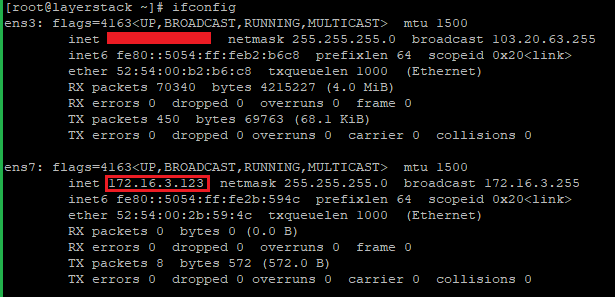
CentOS – 8
Edit the network configuration file using the below command.
# /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth1
Note: eth1/ens1 is the device name of the server. Please replace with the correct device name if necessary.
Add the following entries for the network card and configure the preferred private IP address.
The following IP ranges are required to use as private IP addresses:
10.0.0.0/8
172.16.0.0/16
192.168.0.0/24
Example for 172.16.3.123:
DEVICE=eth1 ONBOOT=yes BOOTPROTO=static IPADDR=172.16.3.123 NETMASK=255.255.255.0 USERCTL=no
Note: The netmask of LayerStack private IP range is /24 subnet (255.255.255.0).
Save the file.
Restart the network service and make the changes effect.
# systemctl restart NetworkManager.serviceCheck the private IP address configured properly inside the network card.
# ifconfig
CentOS – 6 / 7
Edit the network configuration file using the below command.
# /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth1
Note: eth1/ens1 is the device name of the server. Please replace with the correct device name if necessary.
Add the following entries for the network card and configure the preferred private IP address.
The following IP ranges are required to use as private IP addresses:
10.0.0.0/8
172.16.0.0/16
192.168.0.0/24
Example for 172.16.3.123:
DEVICE=eth1 ONBOOT=yes BOOTPROTO=static IPADDR=172.16.3.123 NETMASK=255.255.255.0 USERCTL=no
Note: The netmask of LayerStack private IP range is /24 subnet (255.255.255.0).
Save the file.
Restart the network service and make the changes effect.
# systemctl restart network.serviceCheck the private IP address configured properly inside the network card.
# ifconfig
Debian
Edit the network configuration file using the below command.
# /etc/network/interfacesAdd the following entries for the network card and configure the preferred private IP address.
The following IP ranges are required to use as private IP addresses:
10.0.0.0/8
172.16.0.0/16
192.168.0.0/24
Example for 172.16.3.123:
auto ens4 iface ens4 inet static address 172.16.3.123 netmask 255.255.255.0
Note: The netmask of LayerStack private IP range is /24 subnet (255.255.255.0).
Save the file.
Restart the network service and make the changes effect.
# systemctl restart network.serviceCheck the private IP address configured properly inside the network card.
# ip addr
Ubuntu
Edit the network configuration file using the below command.
# /etc/network/interfacesAdd the following entries for the network card and configure the preferred private IP address.
The following IP ranges are required to use as private IP addresses:
10.0.0.0/8
172.16.0.0/16
192.168.0.0/24
Example for 172.16.3.123:
auto eth1 iface eth1 inet static address 172.16.3.123 netmask 255.255.255.0
Note: The netmask of LayerStack private IP range is /24 subnet (255.255.255.0).
Save the file.
Restart the network service and make the changes effect.
# systemctl restart network.serviceCheck the private IP address configured properly inside the network card.
# ifconfig
Ubuntu 17.10 and higher versions use NetPlan as the default network management tool and its configuration files are written in YAML syntax with a .yaml file extension.
Edit the network configuration file using the below command.
# vi /etc/netplan/50-cloud-init.yamlAdd the following entries for the network card and configure the preferred private IP address.
The following IP ranges are required to use as private IP addresses:
10.0.0.0/8
172.16.0.0/16
192.168.0.0/24
Example for 172.16.3.123:
network: version: 2 renderer: networkd ethernets: ens7: dhcp4: no addresses: [172.16.3.123/16]
Note: The netmask of LayerStack private IP range is /24 subnet (255.255.255.0) & change the name of the ethernet interface as on your server.
Update networking with the below command and then the changes will take effect.
# netplan applyCheck the private IP address configured properly inside the network card.
# ifconfig
Fedora
Edit the network configuration file using the below command.
# /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth1
Note: eth1/ens1 is the device name of the server. Please replace with the correct device name if necessary.
Add the following entries for the network card and configure the preferred private IP address.
The following IP ranges are required to use as private IP addresses:
10.0.0.0/8
172.16.0.0/16
192.168.0.0/24
Example for 172.16.3.123:
DEVICE=eth1 ONBOOT=yes BOOTPROTO=static IPADDR=172.16.3.123 NETMASK=255.255.255.0 USERCTL=no
Note: The netmask of LayerStack private IP range is /24 subnet (255.255.255.0).
Save the file.
Restart the network service and make the changes effect.
# systemctl restart NetworkManager.serviceCheck the private IP address configured properly inside the network card.
# ip a
